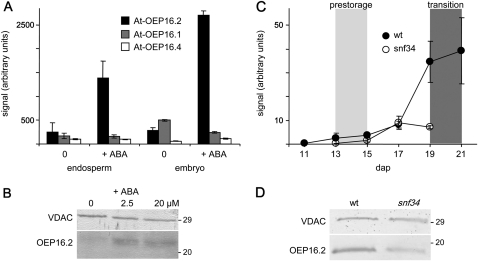
Fig. 5.
Specific ABA induction of OEP16.2 expression in seeds. (A) Digital northern blot of At-OEP16.2 (black), At-OEP16.1 (grey), and At-OEP16.4 (white) expression (arbitrary units) in Arabidopsis endosperm and embryo tissue. Prior to dissection, seeds were germinated for 24 h without (0) and with 20 μM ABA (described in Penfield et al., 2004). Data used to create the expression profile were obtained from the analysis by Penfield et al. (2004) using NASCArrays database (http://affy.arabidopsis.info/narrays/experimentbrowse.pl), experiment NASCARRAYS 386. Signal intensities were averaged from three biological replicates (n=3, ±SD). (B) Western blot analysis of At-OEP16.2 in protein extracts (7.5 μg each) from Arabidopsis seeds, germinated for 48 h on medium containing 0, 2.5, and 20 μM ABA. (C) Transcript content of Ps-OEP16.2 (n=2, ±SD, arbitrary units) in developing pea seeds of the wild type (black) and the Vf-SnRK1-antisense line snf34 (white). The age of seeds is given in days after pollination (dap). According to the definition by Radchuk et al. (2006), delayed down-regulated genes are highly expressed in the pre-storage phase 13–15 dap (light grey area), and delayed up-regulated genes are continuously increased during seed maturation, starting in the transition phase at 19–22 dap (dark grey area). (D) Immunoblot analysis of Ps-OEP16.2 in protein extracts (4 μg each) from wild-type and VfSnRK1-antisense (snf34) pea seeds, isolated 20 dap. (B and D) Antiserum against the marker protein VDAC (outer membrane of mitochondria) was used as a loading control. Numbers indicate the molecular mass of proteins in kDa.