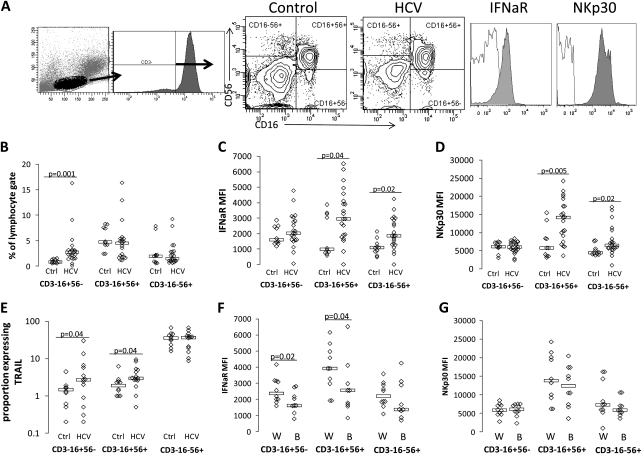
Figure 1.
Natural killer (NK) subset interferon (IFN)–αR expression is increased during hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, and expression differs by race. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stained with CD3, CD16, CD56, IFN-αR, and NKp30 or isotype control, and flow cytometric analysis was performed on a BD LSRII. A, Gating strategy used to define NK cell subsets in both healthy control and HCV-infected subjects, followed by example of IFN-αR and NKp30 expression on NK cells of 1 healthy control subject. Isotype shown in nonshaded area, and antibody shown in shaded area. Specific NKp30 and IFN-αR expression were determined as mean fluorescence intensity above isotype control. NK subset frequency (B), IFN-αR (C), NKp30 (D), and TRAIL (E) expression comparison between healthy control subjects (ctrl; n = 10) and HCV-infected patients (n = 21). IFN-αR (F) and NKp30 (G) are shown as a function of race in the HCV-infected group (W = white, B = black). P values ≤.05 are shown.