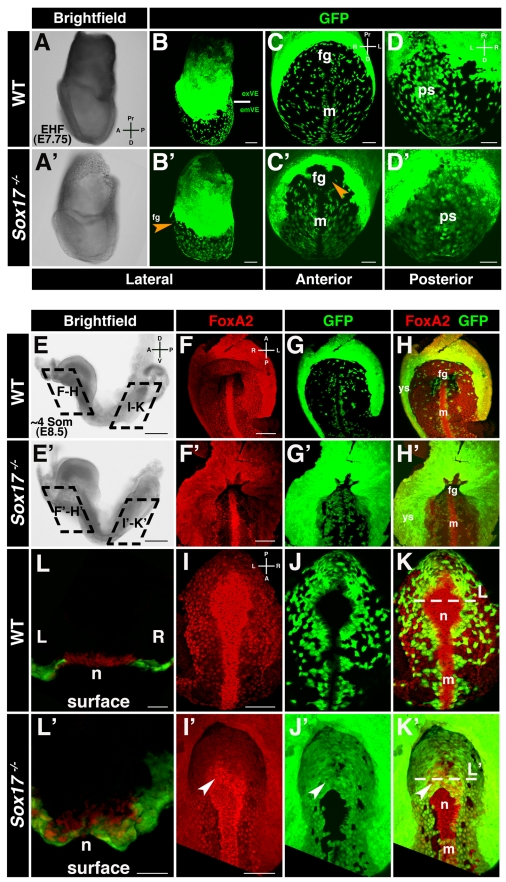
Figure 2. Sox17 mutants exhibit a failure in emVE dispersal.
(A and B) Brightfield image and maximum intensity projection (MIP) of confocal z-stacks of wild-type Afp::GFP (panVE-reporter) embryo at EHF. Solid white line demarcates the boundary between extraembryonic (ex) and embryonic (em) regions. (C and D) Anterior and posterior views of embryonic regions of the embryo in (B), depicting dispersed emVE cells laterally, absence of GFP at midline, and uniform distribution of GFP-positive cells overlying primitive streak. (A′–D′) Brightfield and MIPs of EHF stage Sox17 −/− ; Afp::GFPTg/+ embryo. A near-uniform layer of GFP-positive cells is present in extraembryonic and embryonic regions. GFP was absent in the midline and the area of the prospective anterior intestinal portal (orange arrowheads). (E and E′) ∼4 somite stage wild-type and Sox17 mutants are comparable by gross morphology. (F–H) MIPs reveal uniform GFP in yolk sac, dispersed GFP-positive emVE cells in gut endoderm, and absence of GFP in midline of wild-type embryos. (F′–H′) In the Sox17 mutant, while some GFP-negative areas are present, undispersed GFP-positive cells predominate in the gut endoderm around the anterior intestinal portal. Additionally, the distance from the foregut invagination to the yolk sac was decreased. (I–K) Posterior views of wild-type embryo, scattered GFP-positive emVE cells in gut endoderm, and emergent node. (I′–K′) Mutants exhibit homogeneous GFP-positive cells. Additionally, GFP-positive cells cover part of the node (white arrowheads). (L and L′) Sections through node depict FoxA2-positive cells emergent on embryo's surface in wild-type, but some remaining covered by GFP-positive cells in mutant. fg, foregut; m, midline; n, node; ps, primitive streak; ys, yolk sac; exVE, extraembryonic VE; emVE embryonic VE; A, anterior; D, distal (in panels A, C, and D); D, dorsal (in panel E); L, left; P, posterior; Pr, proximal; R, right; V, ventral. Scale bars = 200 µm in (E and E′); 100 µm in (B, B′, F, F′, I, and I′); and 50 µm in (C, C′, D, D′, L, and L′).