Figure 1.
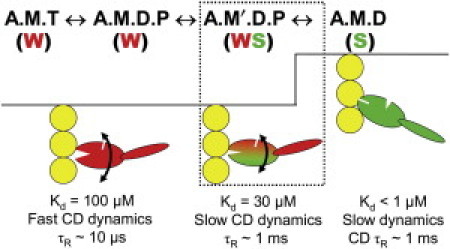
Model for coupling of actomyosin ATPase to force and movement, focusing on the coupling of biochemical transitions to orientation and dynamics of the myosin catalytic domain, adapted from Thomas et al. (4). (Red and green) Weak (preforce) and strong (force-bearing) complexes respectively. (Curved arrows) Orientational disorder. An upward step indicates the power stroke. Text at top indicates the biochemical state (defined by the active site ligand): A, actin; M, myosin; T, ATP; D, ADP; P, inorganic phosphate. Prime (′) indicates a second structural state corresponding to the same biochemical state. Text under each state indicates distinguishing properties of the catalytic domain.
