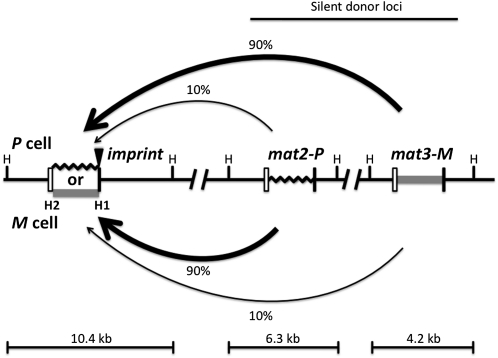
Figure 1 .
The directionality phenomenon of mating-type switching in fission yeast. The diagram shows mat1, mat2P, and mat3M genes located from left to right in chromosome 2. The mat1 locus is expressed and it confers cell type, while mat2P and mat3M, located in the silenced region, act only as donors for providing copies of genetic information for mat1 switching. The mat1 can be either P (black zigzag line, representing 1104-bp-long DNA sequence) or M (shaded bar, 1128 bp). Each mat cassette is flanked by the homology regions, boxes H2 (left open box, 135 bp) and H1 (right solid box, 59 bp), which are used for switching-promoted recombination. The imprint site (solid triangle) is located at the junction of the mat1 allele-specific and the H1 box sequences. The donor preference is determined by the mat1 cell type; mat1-P cells choose mat3 and mat1-M cells choose mat2, both with ∼90% preference (thick arrow) over the other, less-preferred (∼10%, thin arrow) donor locus. The HindIII restriction enzyme sites (H) flanking each cassette are shown. Digestion of yeast genomic DNA with the restriction enzyme generates three fragments of indicated sizes, each containing a specific mat locus. The figure is not drawn to scale.