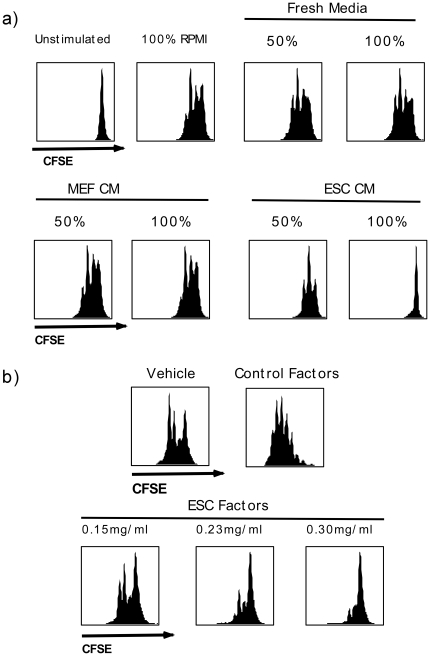
Figure 1. ESC-conditioned media and cellular factors from ESC-extracts inhibit T cell proliferation in response to anti-CD3/anti-CD28 stimulation.
a) C57BL/6 splenocytes were labeled with CFSE and activated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 in RPMI media (unstimulated cells presented in panel 1 and stimulated cells in panel 2). Cells were also activated in 50% RPMI along with 50% or 100% fresh unconditioned media (panels 3 and 4), 50% RPMI along with 50% or 100% mouse embryonic fibroblast-conditioned media (MEF-CM, panels 5 and 6), and 50% RPMI along with 50% or 100% mouse ESC-conditioned medium (ESC-CM, panels 7 and 8). After 48 hours the cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for proliferation. b) ESCs were grown in feeder free cultures, harvested and lysed by sonication. Cell membrane, mitochondria and nucleus were removed by centrifuging the sonicate at 15000 g for 15 minutes. Proliferation of B6 splenocytes stimulated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 in RPMI media was assessed using extraction buffer alone (vehicle, panel 1), lysates from C2C12 cells (Control-Factors) or increasing concentration of ESC-derived factors (ESC-Factors). Results are representative of 4 separate experiments.