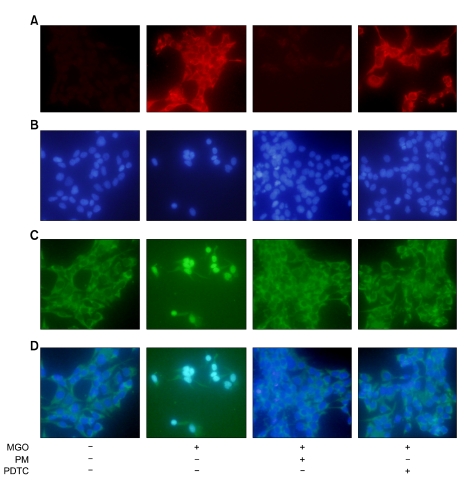
Figure 3.
Argpyrimidine formation and subcellular localization of the NF-κB p65 subunit in HLE-B3 cells. (A) Immunofluorescence staining of argpyrimidine. (B) Fluorescent counterstaining of nuclei with DAPI. (C) Subcellular localization of the NF-κB p65 subunit. (D) Merge of the signals for NF-κB p65 subunits and DAPI. HLE-B3 cells are incubated with the indicated concentration of MGO in the presence or absence of PDTC for 24 h. In control cells, NF-κB is located in the cytoplasm. In cells treated with MGO for 24 h, argpyrimidine (AP) formation is induced by MGO and NF-κB is translocated into the nuclei. However, both PM and PDTC inhibit NF-κB nuclear translocation.