Figure 4. Effects of microglial depletion on palmitic acid-induced TNFα and IL-6 release.
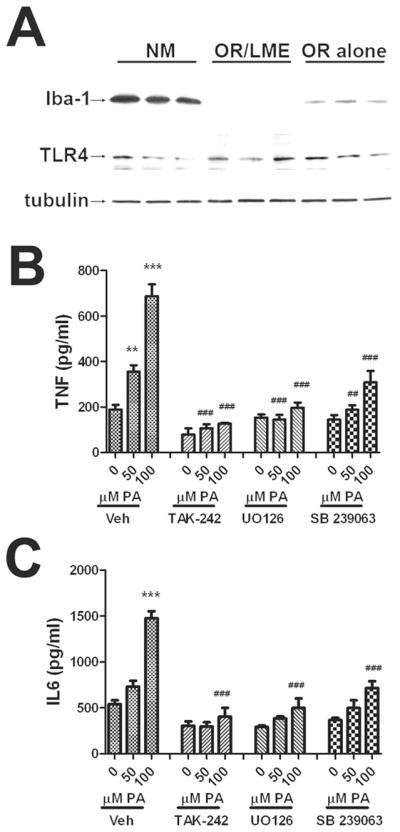
Cultured astrocytes were subjected to either no manipulation (NM), orbital rotation (OR alone), or orbital rotation followed immediately by exposure to LME (OR/LME) as described in Methods. (A) Representative images of Western blots depicting expression of the microglial marker Iba-1 (top panel), TLR4 (middle panel), and tubulin (bottom panel) in cultured cells subjected to the different manipulations. Release of (B) TNFα or (C) IL-6 from cells subjected to orbital rotation followed by LME that were treated with increasing does of palmitic acid in the presence or absence of inhibitors of TLR4 (TAK-242, 5 μM), p42/44 MAPK (UO126,5 μM), or p38MAPK (SB 239063, 5 μM). All inhibitors were applied to cells 45 min before administration of BSA or palmitic acid. Data were compiled from 2–4 separate experiments, and are means and SEM of 10–20 dishes per group. ** and *** indicate significant (p<0.01, and p<0.001, respectively) increases in cytokine release from microglia-depleted astrocytes treated with palmitic acid as compared to control cells treated with BSA. ## and ### indicate significant (p<0.01, and p<0.001, respectively) decreases in cytokine release from astrocytes treated with palmitic acid in the presence of TAK-242, UO126, or SB 239063 as compared to cells treated with the same dose of palmitic acid alone.
