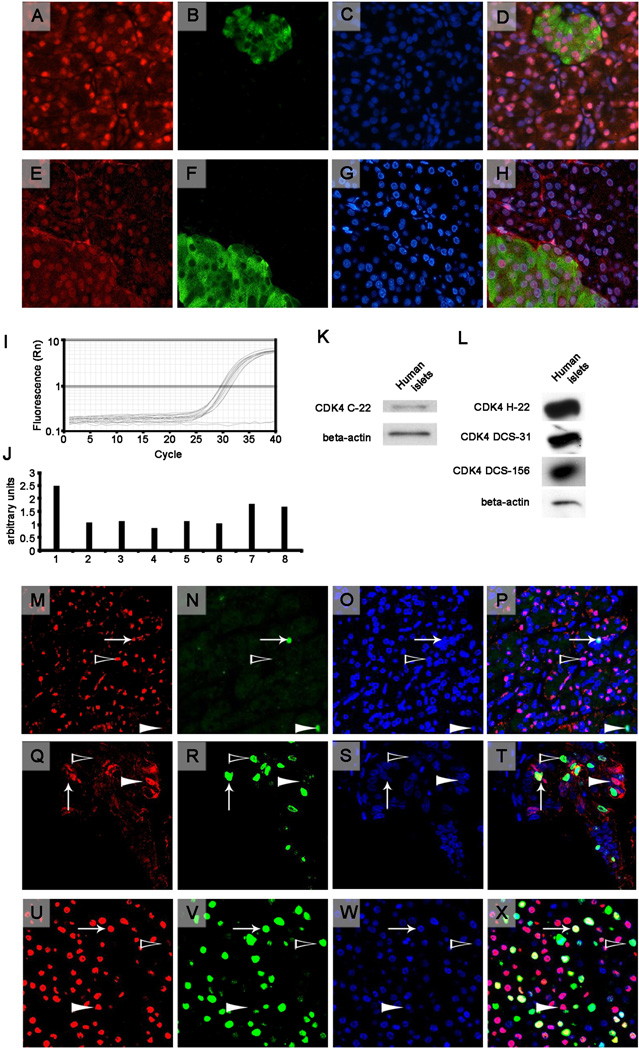
Figure 1.
Top Panels (A-H). Two representative sections of healthy human pancreas from the UTIP healthy series (A-H) immunostained for CDK4 (A, E) and co-stained with insulin (B, F) and the nuclear marker Hoechst (Sigma) (C, G) for nuclear detection. Each row corresponds, from left to right, to the same section that was stained for CDK4 using the C-22 antibody (A) or the H-22 antibody (E) in red (Cy3), insulin in green (B, F) (Cy2) and nuclear staining with Hoechst in blue (C, G). The images were then merged (D, H). Images are at 40× magnification using an epifluorescence microscope. Middle panels (I-L). Real-time PCR (I, J) and western blot analysis (K, L) for CDK4 in human islets. I: Graphic representation of the fluorescence vs. the cycles of real-time PCR for CDK4 for 8 different samples of human islets (in triplicate) and a negative control (no sample, plain line, in duplicate). J: Quantification of the intensity that was obtained using real-time PCR and normalized to a housekeeping gene (TBP). K: Representative western blots of CDK4 (C-22 antibody) and beta-actin in human islets. L: Representative western blots of CDK4, which was performed with the H-22 antibody, the DCS-31 antibody or the DCS-156 antibody, and beta-actin in human islets. Bottom panels (M-X). Representative CDK4-positive cores from the PAC481 array showing a healthy human pancreas (M-P) and two different adenocarcinoma cores (Q-T, U-X). From left to right, images of the same section that were stained for CDK4 (C-22 antibody) in red (Cy3), the proliferation marker Ki-67 in green (Cy2), nuclear staining with Hoechst in blue, and a merge of all images are shown. An arrow indicates a CDK4- and Ki-67-positive nucleus, a white arrowhead indicates a CDK4-positive and Ki-67-negative nucleus, and a black arrowhead indicates a CDK4-negative and Ki-67-positive nucleus. Images were taken at 40× magnification using a confocal microscope.