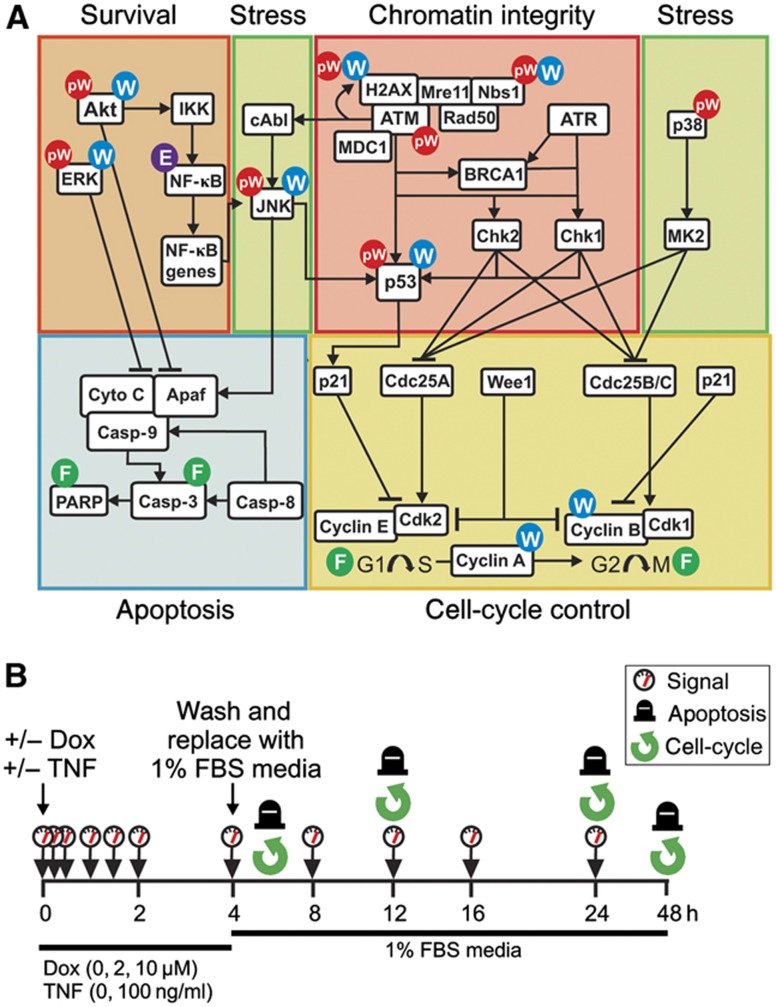
Figure 1.
A strategy for systematic analysis of signal transduction pathways involved in the DDR. (A) An expanded DNA damage signaling network that reports on internal cellular states and external microenvironment cues indicating the intersection and integration of multiple distinct signaling pathways that respond to or modulate chromatin integrity, cellular stress, survival, apoptosis, and cell-cycle progression or arrest. Indicated nodes and responses in this expanded DNA damage-response network were interrogated by quantitative western blotting for the total (W) or phospho-forms (pW) of signaling molecules, ELISA-based activity assay (E), or flow cytometry (F). (B) Experimental approach: cells were treated +/− doxorubicin (Dox; 0, 2, or 10 μM) and +/− TNFα (0 or 100 ng/ml) for 4 h. Four hours following treatment, the media was replaced with fresh media containing 1% FBS. Cell extracts for signal measurement were collected at 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 4, 8, 12, 16, and 24 h following treatment. Whole cell samples were collected and fixed for cellular-response measurements at 6, 12, 24, and 48 h following treatment.