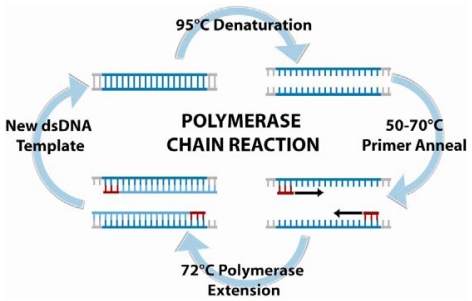
Figure 5.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an amplification-based technique for DNA detection. The standard protocol involves raising the temperature of the reaction to 95 °C to separate the DNA strands, lowering to the annealing temperature for the oligonucleotide primers to hybridize, and then raising to the optimal DNA polymerase temperature 72 °C for primer extension. This process is repeated cyclically, creating many copies of the target sequence.