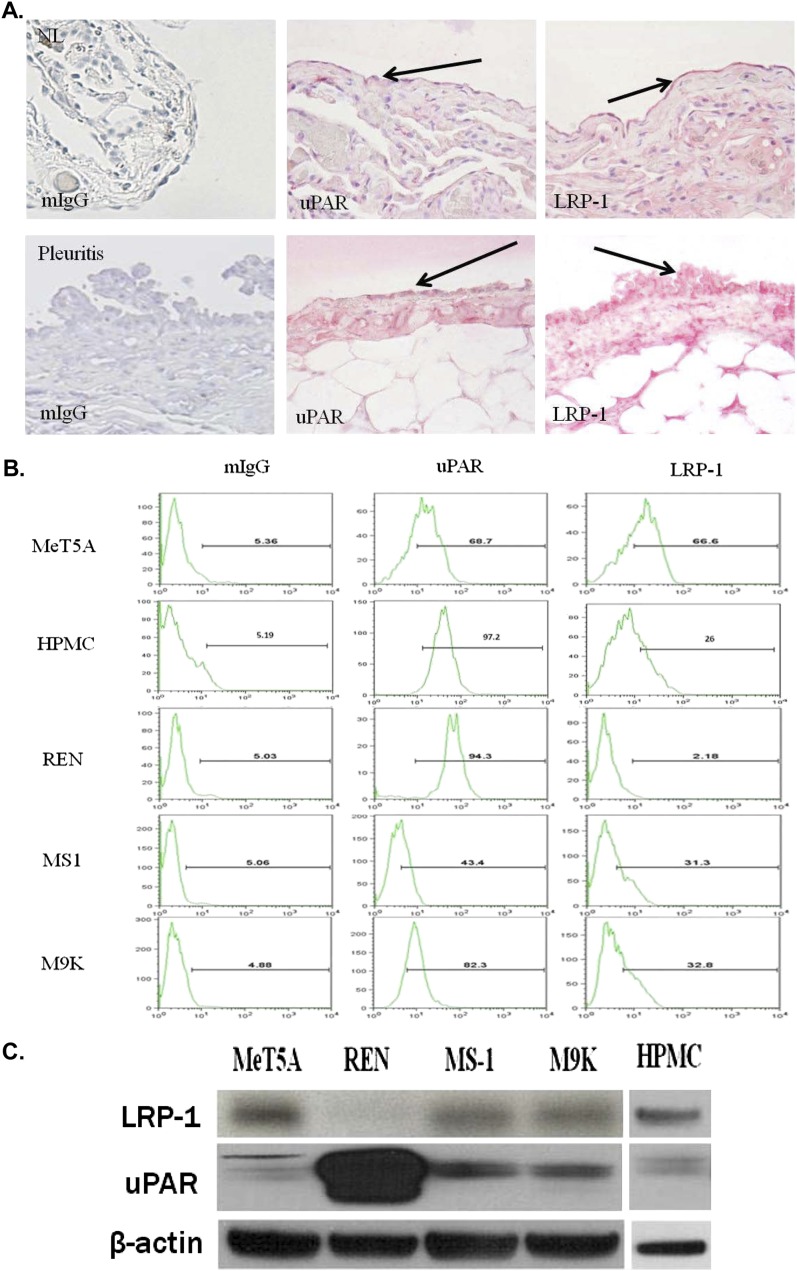
Figure 1.
Analysis of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) and lipoprotein receptor–related protein (LRP) expression in human lung tissues, in pleural mesothelial cells (PMCs), and malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) cells. (A) Tissue sections were prepared from the lungs of patient without lung disease and a patients with pleuritis. The sections were probed for the expression of uPAR and LRP-1 by the pleural mesothelial cell lining using immunohistochemical analysis. The sectioned pleural mesothelium in its entirety was analyzed for uPAR and LRP-1 expression. The arrows indicate Fast-red staining of uPAR and LRP-1 in the pleural mesothelium. NL indicates the findings in representative normal lung visceral pleura, which shows underlying compressed lung parenchyma. The parietal pleural surface from the patient with pleuritis best illustrated reactivity for each antigen and is shown accordingly. Original magnification, ×40. (B) Serum-starved MeT5A cells, human pleural mesothelial cells (HPMCs) and REN, MS-1, and M9K MPM cells were probed with mouse monoclonal antibodies against uPAR and LRP-1 and analyzed via FACS analysis. The data are presented as a representative histogram of three independent experiments. (C) Serum-starved MeT5A, REN, MS-1, M9K, and HPMC cell lysates were probed for LRP-1 light chain expression (85 kD) and uPAR or β-actin loading controls via Western blot analysis.