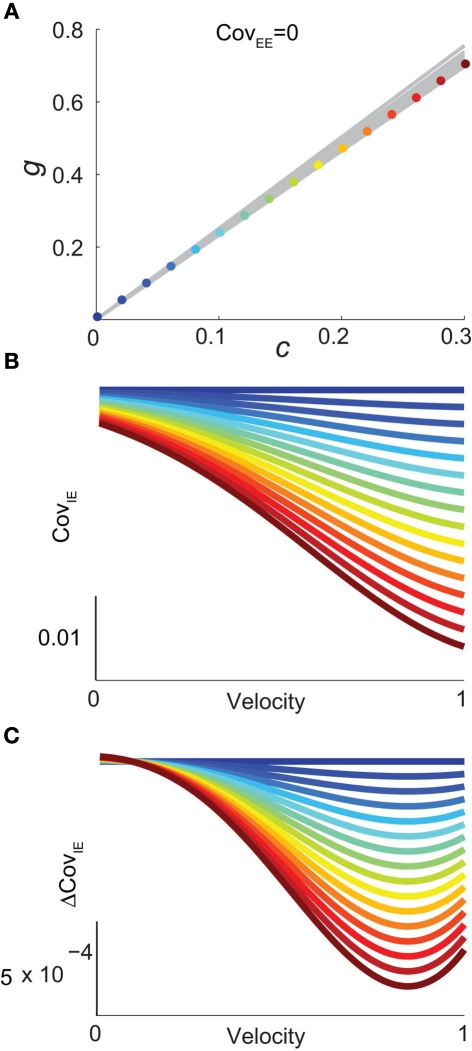
Figure 6.
Analysis of I-E statistics in the binary model. (A) With the analytic approximation for CovEE (equation (14)), we plot the region of parameter space (c, g) where CovEE ≈ 0, with each gray line representing a particular velocity (ranging from 0 to 1, see Figure 4). Larger values of c correspond to larger g values. Color-coded dots are a representative subset of (c, g) pairs used below in (B,C). (B) The analytic formula for CovIE (equation (15)) enables analysis of how it changes with velocity for a particular pair of c and g values (colored coded). Although many (c, g) pairs give CovEE ≈ 0, larger values exhibit more of a decrease in CovIE with velocity (the decrease is of the same order as the full binary network and LIF simulations). (C) A similar analysis for the width of the histogram of CovIE (see equation (16)) values, again, shows that large c and g values correspond to more of a decrease in the width of this distribution in the evoked state. Except for c and g, the parameters for the binary model match those used in (Figure 4).