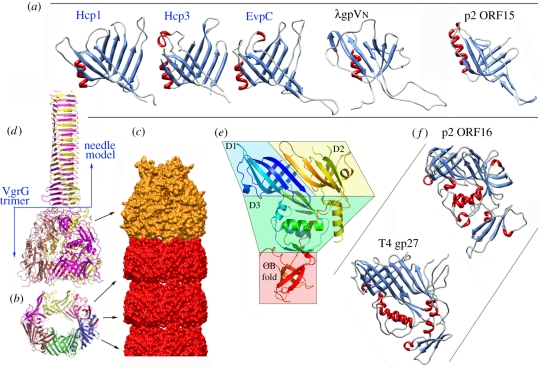
Figure 2.
Structure of the tail tube proteins. (a) Ribbon views of the three Hcp proteins of known structures and their bacteriophage homologues (colours according to secondary structures). (b) Ribbon view of the hexameric ring of Hcp. (c) The tube surface model formed of stacked Hcp rings (red) and terminated by a VgrG trimer (orange). (d) Ribbon view of the VgrG trimer (ribbons, colours per monomer) as determined experimentally by X-ray diffraction and the molecular model of the needle domain (modelled from the bacteriophage T4 gp5) attached to it. (e) Ribbon view (rainbow colours from blue (Nt) to red (Ct)) illustrating the VgrG domain topology: the two β-sandwich domains (D1, D2), the α/β domain (D3) and the OB fold. (f) Ribbon view of bacteriophage structural homologues of VgrG (colours according to secondary structures). Figures were drawn with PyMOL [24] or Chimera [25].