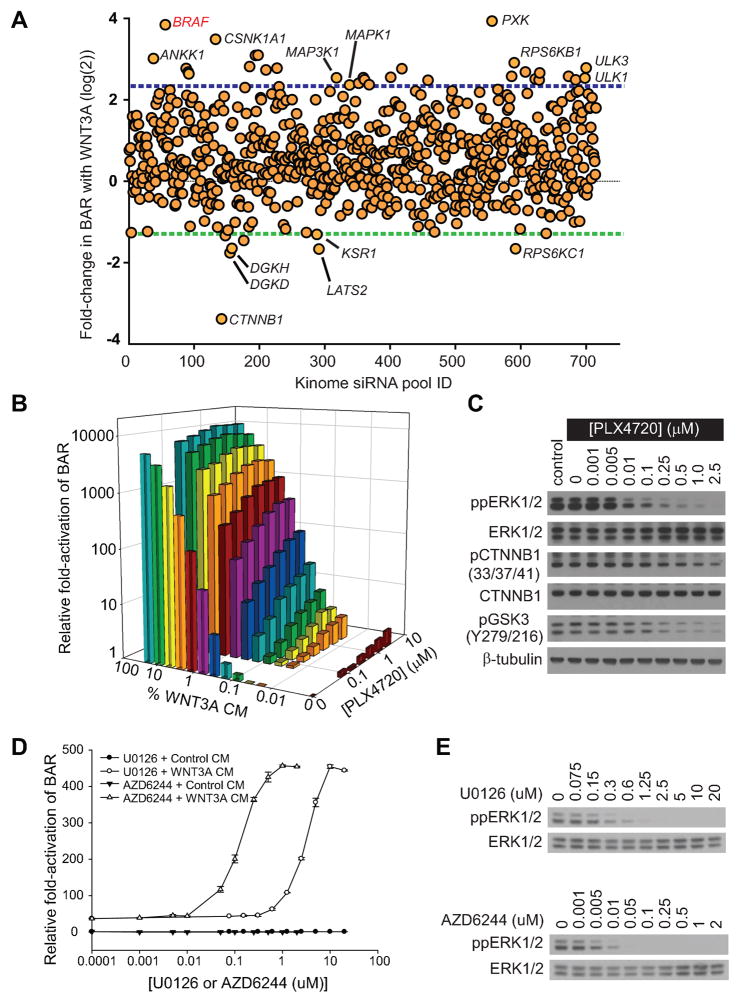
Figure 1. BRAF signaling negatively regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in melanoma cells.
A) Scatter plot of a kinome-based siRNA screen in human A375 melanoma cells stably expressing the β-catenin-activated reporter (BAR) driving firefly luciferase, with each dot representing a known or predicted kinase. Blue- and green-dotted lines represent two mean absolute deviations above and below the mean, respectively. The full gene list is presented in Supplementary database S1–S2. B) An isobologram analysis shows a dose-dependent enhancement of Wnt/β-catenin signaling with the targeted BRAF inhibitor PLX4720 and WNT3A CM on BAR activity. C) Immunoblot analysis of the dose-dependent inhibition of dual-phosphorylated ERK1/2 (ppERK1/2), phosphorylated Ser33/Ser37/Thr41 β-catenin (pCTNNB1), and phosphorylated Tyr216 GSK3 following PLX4720 treatment. D) Two distinct MEK inhibitors, U0126 and AZD6244, both enhanced Wnt/β-catenin signaling in a dose-dependent manner. Symbols and error bars represent the mean and standard deviation, respectively, of three biologic replicates E) Immunoblot analysis of the dose-dependent inhibition of ppERK1/2 by MEK1/2 inhibitors U0126 and AZD6244. In (B–E), A375 cells were treated for 24 hours with the indicated conditions prior to harvesting and data are representative of at least three independent experiments.