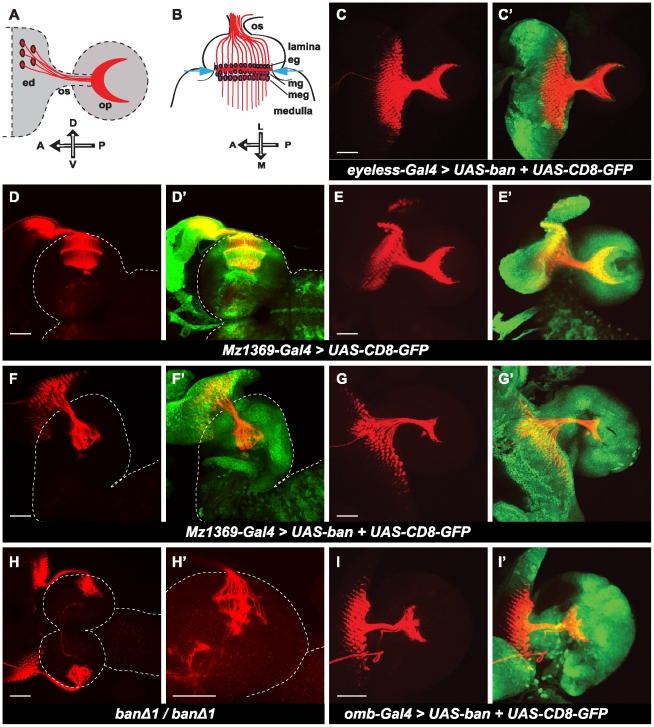
Figure 3. bantam affects photoreceptor-neuron axon projection in the optic lobe.
(A, B) Schematic illustration of the photoreceptor (R1–R8) axon projection patterns in the late third instar larval brain of Drosophila. (A) A lateral view of axons from photoreceptor neurons (R1–R8) (red) in the eye disc (ed) projecting through the optic stalk (os) into the optic lobe (op). The projection pattern of R axons in the optic lobe is crescent shaped (red). (B) A horizontal view of axons (red) of R cells projecting into different layers of the optic lobe. Axons from R1–R6 (red) stop between two layers of glial cells in the lamina, the epithelial (eg) and marginal glial cells (mg) (magenta), and form the lamina plexus (red line between two blue arrows). R7 and R8 project deeper into the medulla (A: anterior; P: posterior; D: dorsal; V: ventral; L: lateral; M: middle). The anti-Chaoptin (red) was used to view R-cell projection patterns. UAS-CD8-GFP (green) was used to visualize expression patterns of Gal4 drivers. Brain surface is outlined by dashed lines. (D, D′, F, F′, H, H′) Brains are positioned for a horizontal view. (C, C′, E, E′, G, G′, I, I′) Brains are positioned for a lateral view. (C, C′) over expression of bantam by the eye-specific driver, eyeless-Gal4. (D–E′) wild type brains. (F–G′) over expression of bantam by the optic lobe driver, Mz1369-Gal4. (H, H′) banΔ1/banΔ1 null mutants. (H) Lower magnification shows the two brain hemispheres. (H′) Higher magnification only showing half of a hemisphere. (I, I′) Over expression of bantam by omb-Gal4. Scale bar: 50 µm.