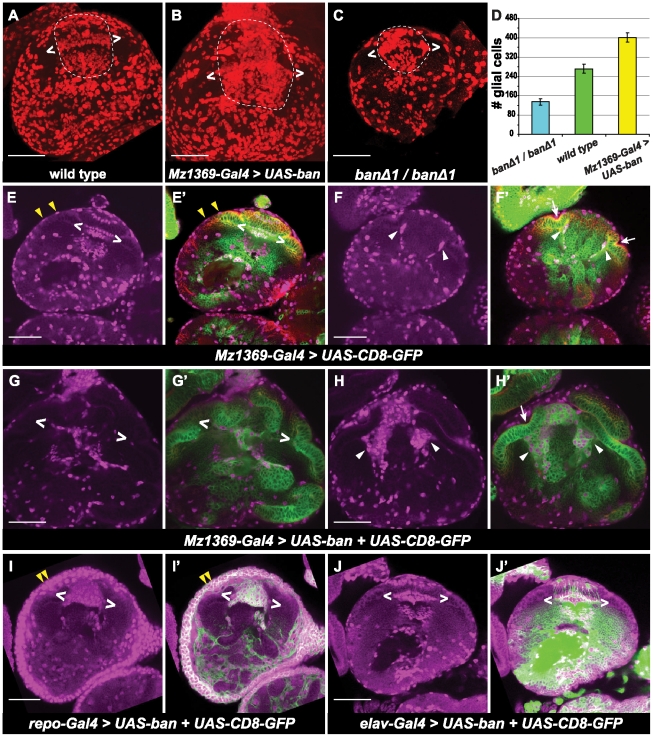
Figure 4. bantam promotes glial cell proliferation in the optic lobe.
All brains are positioned for horizontal views. (A–C) Maximum projection to view total number of glial cells which are stained for anti-Repo (red). Glial cells in the lamina and medulla are circled inside the dashed line. Glial cells between brackets (two white < >) correspond to the three layers of laminal glial cells: epithelial, marginal and medulla glia. (A) wild type brains. (B) over expression of bantam by Mz1369-Gal4. (C) banΔ1/banΔ1 null mutant. (D) histograms of glia number in the optic lobe of the third instar larvae. Glia number were counted in the region circled in A, B, and C. banΔ1/banΔ1 (135±13, n = 5); wild type (272±18, n = 4); Mz1369-Gal4>UAS-ban (402±20, n = 4). (E–J′) A single focal plane is shown. Glial cells are stained by anti-Repo (magenta). UAS-CD8-GFP (green) is used to view the expression of Gal4. Neuroepithelial cells are viewed by anti- DE-cadherin (red). (E–F′) wild type. (G–H′) over expression of bantam by the optic lobe driver, Mz1369-Gal4. (I, I′) over expression of bantam by the glia driver, repo-Gal4. (J, J′) over expression of bantam by the neuron driver, elav-Gal4. (E, E′), (G, G′), (I, I′) and (J, J′) are at a similar focal plane, where three rows of lamina glial cells are present. (F, F′) and (H, H′) are at a similar focal plane, where the lamina furrow (white arrows) and migrating glia (white arrowheads) are present. Cell surface glia cells are indicated by yellow arrow heads. Scale bar: 50 µm.