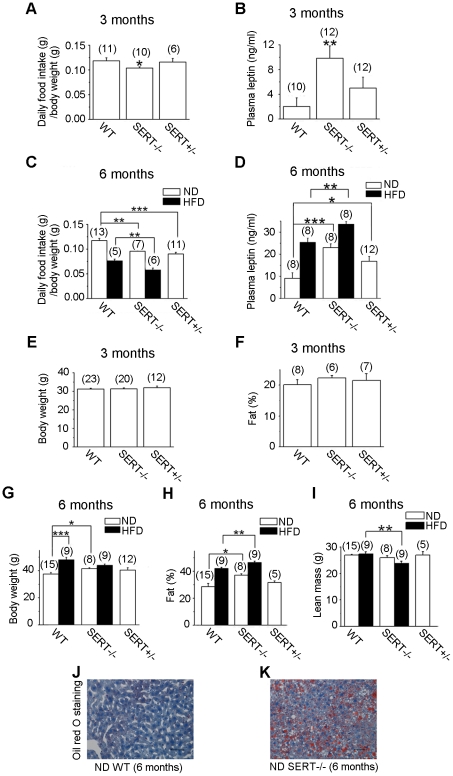
Figure 2. Characterization of food intake and adiposity of SERT-deficient mice.
A and C. Average daily food intake of 3- and 6-month old mice. SERT mutant mice exhibited significantly reduced food intake during ND and HFD feeding, compared to corresponding WT mice. B and D. Quantification of plasma leptin levels in 16 h fasted mice. SERT mutant mice at the age of 3- and 6-month exhibited higher fasting lepin levels, as compared to corresponding WT controls. E. Body weight at age of 3 months. The differences among WT, SERT−/− and SERT+/− mice were not statistically significant. F. Whole-body fat content at age of 3 months. The differences among WT, SERT−/− and SERT+/− mice were not statistically significant. For example, p = 0.34 for the difference between WT and SERT−/− mice, Student's t-test. G. Body weight at age of 6 months. ND-fed SERT−/− mice exhibited higher body weight compared to ND-fed WT. The difference between SERT+/− and WT was, however, not statistically significant. HFD-fed WT mice exhibited higher body weight compared to ND-fed WT mice. However, the difference between HFD- and ND-fed SERT−/− mice was not statistically significant (p = 0.06, Student's t-test). H. Whole-body fat content at age of 6 months. Fat content was increased in SERT−/− mice fed ND and HFD compared to corresponding WT mice. I. Absolute lean mass at age of 6 months. Lean mass was reduced in HFD-fed SERT−/− mice, as compared to HFD-fed WT mice. Data in panels A–I are presented as means ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, Student's t-test. The number of animals analyzed is indicated in parentheses. J and K. Lipid content detected by Oil Red O staining of liver sections of WT and SERT−/− mice. Scale bar, 50 µm.