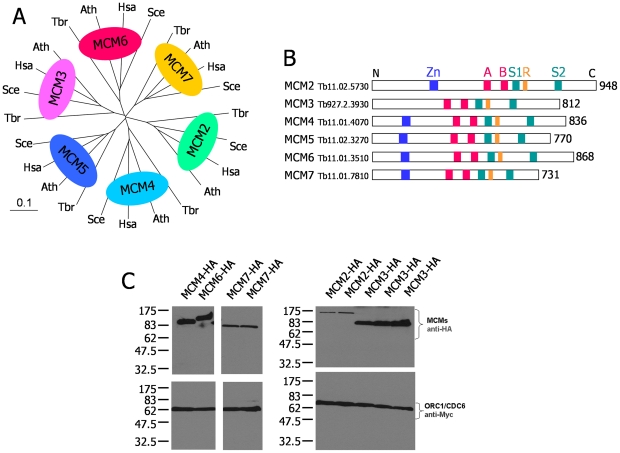
Figure 1. MCM helicase subunits in T. brucei and co-expression with ORC1/CDC6 as epitope tagged variants.
A. An unrooted phylogenetic tree is shown, detailing the homology between predicted MCM helicase subunits in T. brucei (Tbr) relative to orthologues in H. sapiens (Hsa), S. cerevisiae (Sce) and A. thaliana (Ath). Complete protein sequences were aligned with ClustalX, using default settings, and the phylogenetic tree was displayed using TreeView (Page, 1996); the distance corresponding to 10 amino acid changes per 100 positions is indicated (0.1) B. A diagrammatic representation of the MCM helicase subunits in T. brucei. The length of the predicted polypeptides is shown (in amino acid residues), and the position of conserved functional motifs are indicated: an N-terminal Zinc Finger (Zn, blue box); and Walker A and B boxes (A and B, red boxes), an Arginine finger (R, orange box) and sensor 1 and 2 motifs (S1 and S2, green boxes), all involved in nucleotide binding and hydrolysis. C. Western blots of procyclic form TREU 927 T. brucei cells co-expressing C-terminally HA-tagged TbMCM subunits (MCM-HA) and C-terminally Myc-tagged TbORC1/CDC6. The upper panel shows TbMCM-HA expression in whole cell extracts, detected using anti-HA antibody, and the bottom panel shows TbORC1/CDC6-Myc from the same whole cell extracts detected using anti-Myc antibody. Single clones are shown for TbMCM4-HA and TbMCM6-HA, two clones for TbMCM2-HA and TbMCM7-HA, and three clones for TbMCM3-HA. Size markers (kDa) are indicated.