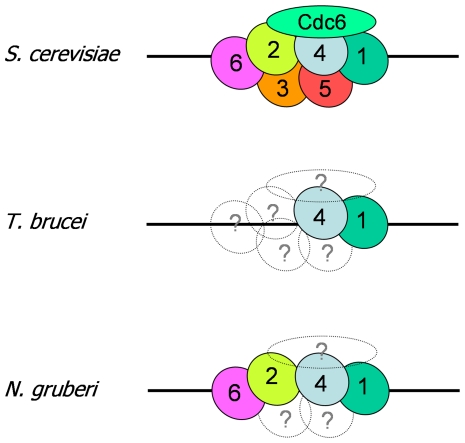
Figure 9. Origin Recognition Complex architecture in the eukaryotes S. cerevisiae, T. brucei and N. gruberi.
The architecture of the Origin Recognition Complex (ORC; composed of Orc subunits numbered 1–6), bound to the Orc1-related factor Cdc6 and to DNA (black line), is shown for S. cerevisiae based on work by Chen et al [22]; the specific arrangement of Orcs 2–5 is inferred from Moreno del-Alamo [58]. In T. brucei, recognisable ORC subunit orthologues are identified, while subunits that are absent or highly diverged are shown as dotted circles containing question marks. The T. brucei ORC subunit indicated as Orc1 appears to be a bi-functional Orc1-Cdc6 protein, and it is unknown if it therefore occupies a distinct architectural position in the ORC or adopts a distinct structure. Putative ORC subunits identified bioinformatically in N. gruberi, a free-living relative of T. brucei, are shown for comparison; here again, Orc1 appears to be an Orc1-Cdc6 fusion.