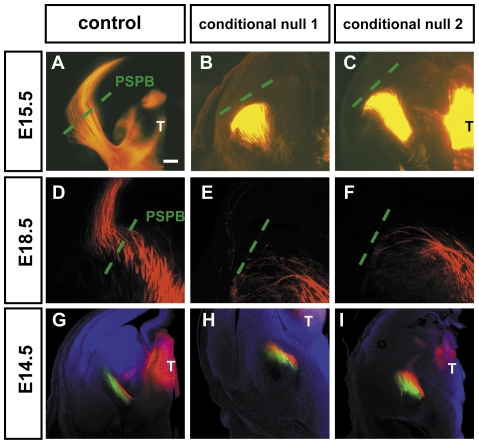
Figure 4. Thalamic axons failed to reach the cortex in Apc conditional null mutants.
(A,D) At E15.5 and E18.5, injections of tracer in control thalamus labelled large bundles of axons projecting from the thalamus (T) through the subpallium and the intermediate zone of the cortex. (B,C) In E15.5 conditional null mutants, thick bundles of axons were observed traversing the subpallium but they stopped before crossing the PSPB and entering the cortex; instead, they changed direction and turned ventrally. (E,F) In E18.5 conditional null mutants, labelled thalamic axons deflected away from the PSPB and cortex. (G–I) In these E14.5 embryos, DiI (red) was injected in rostral thalamus whereas DiA (green) was injected in caudal thalamus (the DiA injection sites are not seen in these planes of section). Nuclei were counterstained with TO-PRO-3 iodide. (G) In controls, the thalamic axons from the rostral thalamus maintain their position medial to axons from the caudal thalamus as they traverse the subpallium. (H,I) Results from two conditional null mutants show that the same order is maintained up to the point at which the thalamic axons halt their progress toward the cortex. Scale bar: A–I, 100 µm.