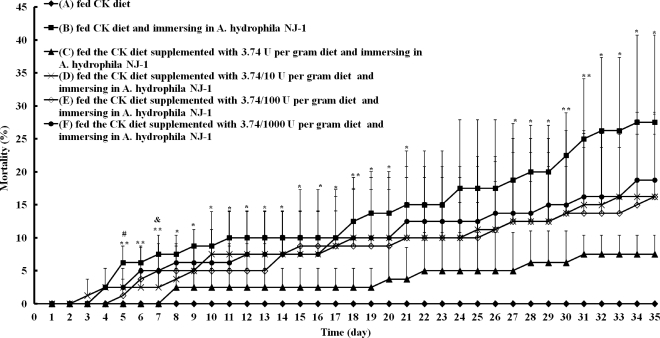
Fig 6.
Determination of the smallest amount of AiiAAI96 needed to protect zebrafish against A. hydrophila NJ-1 infection. Groups were as follows: group A was fed the CK diet and immersed in clean water; group B was fed the CK diet and immersed in A. hydrophila NJ-1-containing water; and groups C, D, E, and F were fed the CK diet supplemented with 3.74, 3.74 × 10−1, 3.74 × 10−2, and 3.74 × 10−3 U AiiAAI96 per gram of feed, respectively, and immersed in A. hydrophila NJ-1-containing water. Each value is the mean ± SD (n = 4). Data marked with * (0.01 < P < 0.05) and ** (P < 0.01) are significantly different between groups B and F, and data marked with # (0.01 < P < 0.05) and & (0.01 < P < 0.05) are significantly different between groups B and C and between groups B and D, respectively.