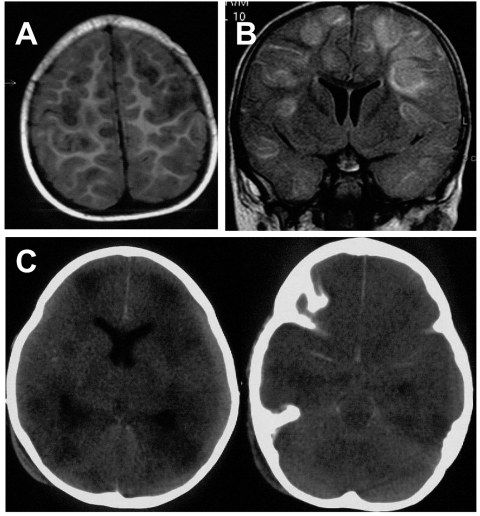
Figure 1.
Axial T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan (A) and coronal fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) (B) show multifocal, mainly cortical and subcortical lesions of high signal intensity, which are most probably caused by multifocal encephalitis. C) Nonenhanced axial computed tomographic (CT) scan performed 2 days after the MRI shows multiple, hypodense lesions and signs of general edema. Additionally, it shows a hyperdense arachnoid collection that was not yet visible on the MRI 2 days before (panels A and B).