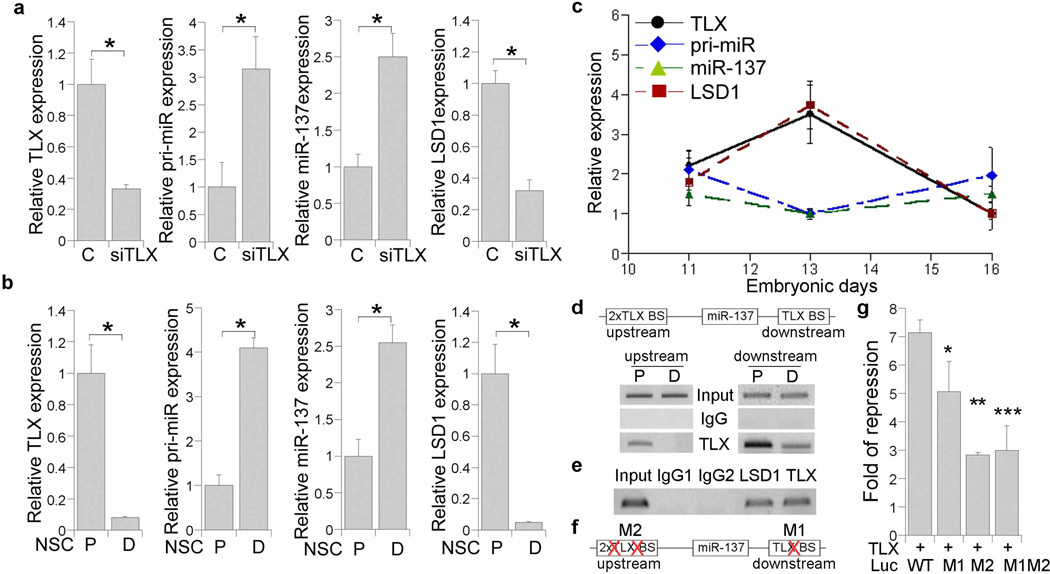
Fig. 6. TLX regulates miR-137 expression.
a. The expression of TLX, the primary precursor of miR-137 (pri-miR), mature miR-137, and LSD1 in control RNA (C) and the TLX siRNA (siTLX)-treated embryonic neural stem cells, as revealed by real time RT-PCR analysis. * p<0.001 by Student’s t-test. n=3. b. The expression of TLX, pri-miR, miR-137, and LSD1 in proliferating embryonic neural stem cells (P) and differentiated neural cells (D), as shown by real time RT-PCR. *p<0.001 by Student’s t-test. n=3. c. The expression of TLX, LSD1, pri-miR-137 (pri-miR), and mature miR-137 at E11, E13, and E16, as shown by real time RT-PCR. d. Binding of TLX to the consensus TLX binding sites (TLX BS) in miR-137 genomic regions, as revealed by ChIP assays. Two consensus TLX binding sites are located at miR-137 upstream and downstream genomic regions. ChIP assays were performed using lysates from neural stem cells that were cultured under proliferation (P) or differentiation condition (D). Input: DNA input; IgG: negative control; TLX: pull down with anti-TLX antibody. e. Recruitment of LSD1 along with TLX to the TLX binding site in miR-137 genomic region as revealed by ChIP assays. Input: DNA input; IgG1, IgG2: negative controls. f. Schematics of the mutants with mutations (X) in the TLX binding sites. g. TLX represses luciferase reporter gene under the control of miR-137 genomic sequences and mutation of the TLX binding sites relieves the repression. WT: wild type TLX binding sites (TLX BS); M1: mutation of the miR-137 downstream TLX BS; M2: mutation of the miR-137 upstream TLX BS; M1M2: mutation of both miR-137 upstream and downstream TLX BS. * p<0.05, **p<0.001, ***p<0.002 by one-way Anova. n=3.