Figure 2. Effect of MUC4-NIDO domain deletion on cell motility, invasion and extravasations.
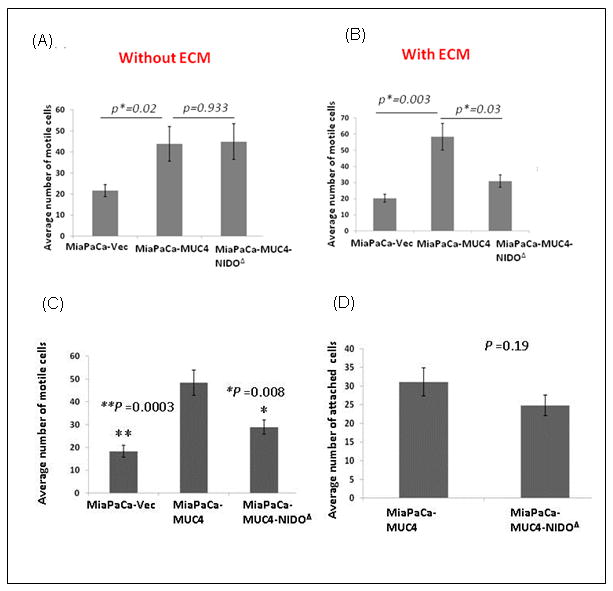
(A) Cell motility assay: 1×106 cells were plated in the top chamber of non-coated polyethylene teraphthalate membranes and incubated for 22 hrs. Cells that transversed the membranes were stained with a Diff-Quick cell staining kit. The number of cells transversing the membrane were determined by averaging 10 random fields of view at 10× and expressed as the average number of cells/field of view and as the average of three independent experiments. Mean+/- SE p<0.05. No significant difference was found between MiaPaCa-MUC4 and MiaPaCa-MUC4-NIDOΔ cells (p= 0.933). (B) The invasion assay was carried out in a similar fashion; except at the place of non-coated trans-well inserts, ECM/Matrigel-coated transwell inserts (BD Biosciences, Bedford, MA) were used. The MiaPaCa-MUC4 cells showed a significantly higher number of invasive cells than MiaPaCa-MUC4-NIDOΔ cells (p=0.03). In both the assays, the MiaPaCa-MUC4 cells showed a significantly higher number of motile (p=0.02) and invasive (p=0.003) cells than the vector control ones. (C) The MiaPaCa-MUC4-NIDOΔ cells show less trans-HUVEC invasion (extravasation) compared to MiaPaCa-MUC4 cells. The number of cells transversing the membrane were determined by averaging 10 random fields of view at 10× and expressed as the average number of cells/field of view and as the average of three independent experiments. Mean+/- SE; p<0.008. (D) The cell-cell adhesion assay showed no significant difference between the number of MiaPaCa-MUC4 and MiaPaCa-MUC4-NIDOΔ cells that adhered to HUVECs (p=0.19).
