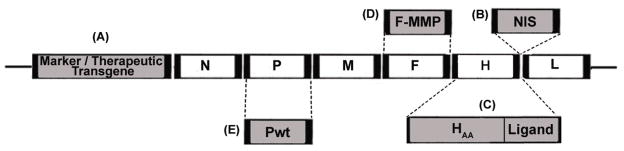
Figure 1.
The unmodified measles virus genome contains the nucleocapsid (N), phospho- (P), matrix (M), fusion (F), hemagglutinin (H) and large (L) genes. A reverse genetics system developed by Radecke et al.[33] allows the engineering of measles virus Edmonston (MV-Edm) strains. A, B: Oncolytic MV-Edm strains can be engineered to express additional transcriptional units. Examples include reporter genes such as the enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) [103], the soluble extracellular N-terminal domain of the human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) [45] and the human lambda light immunoglobulin chain [72], as well as additional therapeutic transgenes such as the prodrug convertase purine nucleotide phosphorylase (PNP) [40, 58] and interferon beta [65] introduced upstream of the viral N gene (A) or the sodium iodide symporter (NIS) gene inserted downstream of the viral H protein [15] (B). The NIS transgene allows noninvasive monitoring of virus localization, replication and gene expression over time and may also be employed as a therapeutic transgene by allowing the intracellular concentration of toxic radioisotopes in infected cancer cells. C: MV-Edm full retargeting can be accomplished via the introduction of H mutations (HAA) that ablate natural entry via the two known measles receptors CD46 and CD150 (signaling lymphocyte-activation molecule; SLAM) [24, 36, 37, 47, 80] and the addition of large peptide sequences (ligands) on the C-terminus of H that allow viral entry and syncytial formation via a wide variety of target receptors [26, 36, 37, 39–41, 43–44, 47, 48, 50, 55, 58, 60, 78, 79, 81–83]. D: Viral retargeting may also be achieved by introducing into the F glycoprotein peptide linkers that are cleavable by specific proteases such as matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) [66]. The modified F protein (F-MMP) can only be efficiently activated by MMPs resulting in restriction of virus tropism to sites that abundantly express theses proteases. E: The defective MV-Edm vaccine strain P gene may be replaced by a wild-type P gene (Pwt) which can more efficiently inhibit innate immune mechanisms resulting in improved oncolytic efficacy [92]. Further modifications include the replacement of the N and L genes by their wild-type counterparts to enhance innate immunity evasion [67].