Figure 6.
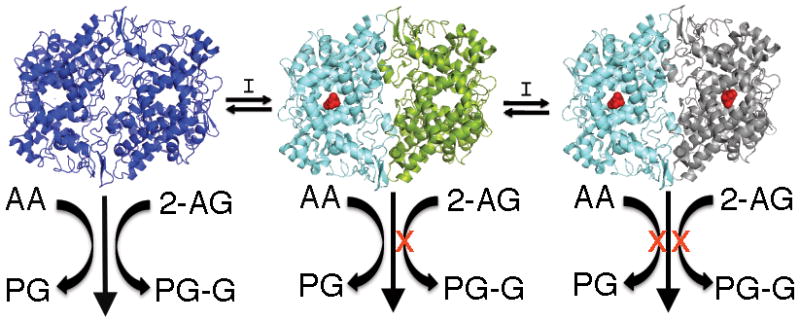
The mechanism of COX-2 substrate-selective inhibition of endocannabinoid oxygenation by rapid, reversible inhibitors. Inhibitor binding in one subunit of the homodimer induces a conformational change in the second subunit that blocks 2-AG and AEA oxygenation but not AA oxygenation. In order to inhibit oxygenation of AA, another molecule of inhibitor must bind in the second subunit. For slow, tight-binding inhibitors, the conformational changes induced by binding a single inhibitor molecule are sufficient to inhibit the oxygenation of all substrates.
