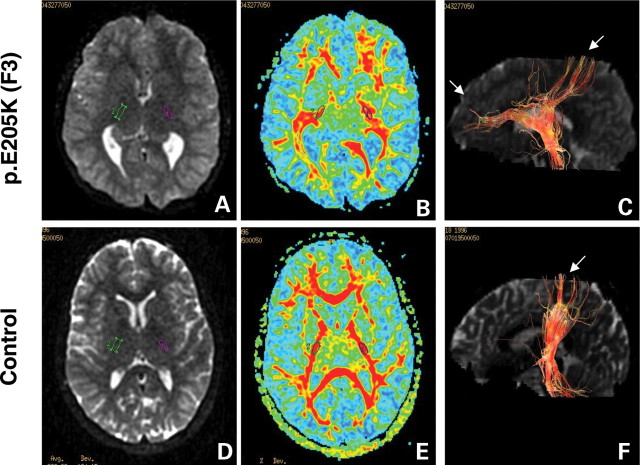
Figure 3.
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of corticospinal tracts in TUBB3 mutation p.E205K (F3) and control individuals. Diffusion-weighted axial images (A and E) show dysmorphic basal ganglia with fusion between caudate and putamen, and virtually no visible anterior arm of the internal capsule, while the posterior arm appears hypertrophic in the patient with TUBB3 mutation (A) compared with control (D). Green and purple circles identify regions of interest (ROI 35 mm2) in the posterior arm of the internal capsule. DTI colour maps (B and E) show the dysmorphic internal capsule in patients with TUBB3 mutation (B) compared with control subjects (F). For all images, colour depicts the predominant fibre direction. The vector analysis of the colour maps is assigned to red (superoinferior), green (anteroposterior) and blue (left to right). The intensities of the colour map are scaled in proportion to the fractional anisotropy (FA). Three-dimensional reconstruction in the sagittal plane of the corticospinal tract at the level of the posterior arm of the internal capsule (C and F) shows progressively smaller tract size and misorientation of the pyramidal fibres, directed in both anteroposterior and superoinferior directions compared (C) with the control patient (F).