Figure 6.
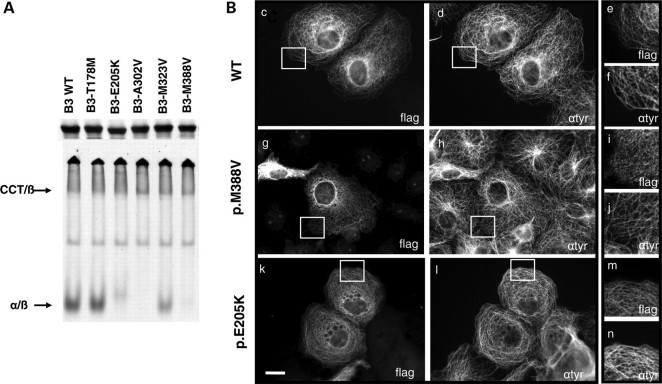
In vitro and in vivo consequences of TUBB3 overexpression in WT and mutants concerning heterodimerization processes and MT incorporation. (A) Mutations in TUBB3 result in inefficient α-/β-tubulin heterodimer formation in vitro. Analysis by SDS–PAGE and non-denaturing gel of in vitro transcription/translation products conducted with 35S-methionine-labelled wild-type (WT) and five different TUBB3 mutants. The reaction products were further chased with bovine brain tubulin to generate α-/β-heterodimers. SDS–PAGE gel showed that the five mutants were translated as efficiently as the wild type control. Note that in non-denaturing gel condition, p.E205K, p.A302V and p.M388V mutants yielded no discernable amount of α-/β-heterodimers. The p.M323V mutant generated heterodimers comparable to WT control and the remaining mutant p.T178M in a diminished yield. (B) Expression of C-terminal FLAG-tagged TUBB3 wild-type (c–f) and mutants [p.M388V (g–i) and p.E205K (k–n)] in transfected COS7 cells revealed by anti-flag (c, g and k) and anti-tyrosinated α-tubulin (d, h and l) staining. Note the limited dotted pattern of the MT network associated with p.E205K and p.M388V mutants overexpression in some cells (i and m) compared with WT (e) and tyrosinated α-tubulin staining (f, j and n). Scale bar: 20 µm (i).