Figure 2.
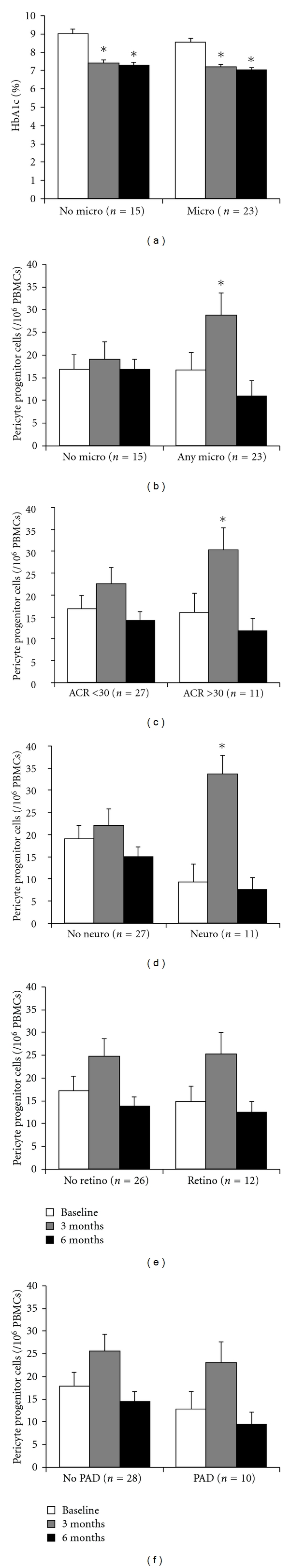
Effects of glucose control on HbA1c and PPCs. (a) There were no differences in HbA1c levels in patients with and without microangiopathy during time (*P < 0.05 versus baseline). (b) Increase in PPC levels was seen only in patients with microangiopathy (ANOVA P < 0.05; *post hoc P < 0.05). (c–f) Patients were divided according to the presence of micro-/macroalbuminuria, neuropathy, retinopathy, and peripheral arterial disease (PAD): a significant PPCs increase was detected in patients with urinary albumin-creatinine ratio (ACR) >30 mg/g and in the presence of neuropathy (ANOVA P < 0.05; *post hoc P < 0.05).
