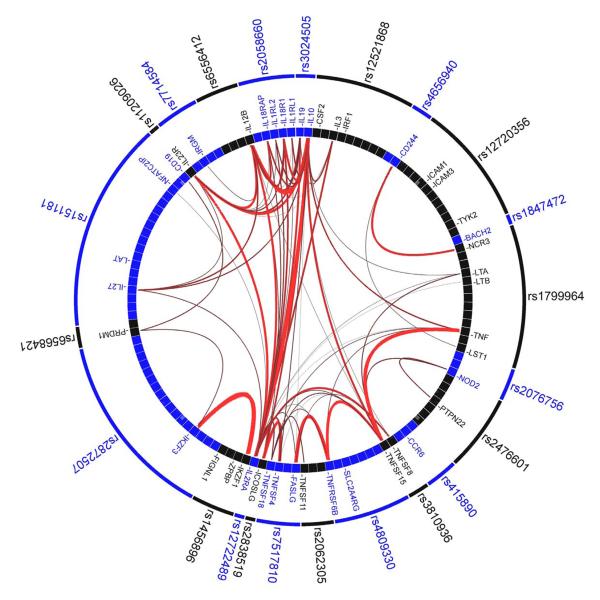
Figure 1. Gene Relationships Across Implicated Loci (GRAIL) pathway analysis.
Links between genes at 23 of 71 Crohn’s disease associated loci which scored P<0.01 using GRAIL. Specifically, of the 71 CD-associated SNPs, 69 are in LD intervals containing or within 50 kb of at least one gene. In total, there are 355 genes implicated by proximity to these 69 SNPs. Each observed CD-association was scored with GRAIL, which takes all genes mapping within CD-associated intervals and evaluates for each whether it is non-randomly linked to the other genes, via word-usage in PubMed abstracts. 23 SNPs shown in the outer circle are P<0.01 hits - indicating that the regions which they tag contain genes which are more significantly linked to genes in the other 68 regions than expected by chance at that level. The lines between genes represent individually significant connections that contribute to the positive signal, with thickness of lines inversely proportional to the probability a literature-based connection would be seen by chance.
To accurately assess the statistical significance of this set of connections, we conducted simulations where we selected 1000 sets of 69 SNPs implicating in total 355 genes ±18 (5%) (selecting the SNPs randomly and using rejection sampling - only taking lists that implicated the same number of genes). Each of those 1000 sets were scored with GRAIL. The mean number of P<0.01 hits in a simulated list was 0.91 with a range in the 1000 sets from 0 to 11, suggesting that the likelihood of observing 23 hits with P<0.01 is far less than 0.1%.