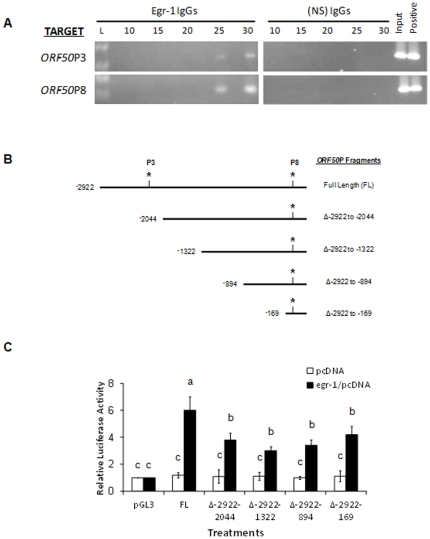
Figure 2. Egr-1 targets KSHV ORF50 in vivo.
(A) BCBL-1 cells were synchronized in S phase [28] and treated with 20 ng/ml of TPA for 8 h. ChIP assays were performed using 2 µg of specific antibodies to Egr-1 or nonspecific IgGs. Primers specifically targeting ORF50P3 or ORF50P8 (see Table 1) were used to perform semi-quantitative PCR experiments on 1% of total DNA (input) and IP samples. Respective cDNA at 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30 cycles were removed and resolved on a 2% agarose gel. IP of BCBL-1 DNA using specific antibodies to histone H3 was used as positive controls. (B) A schematic representation of ORF50P used to make the deletions of the luciferase reporter constructs. The nucleotide locations correspond to the old KSHV genome sequence NC_003409 which has since been updated to NC_009333.1. Asterisks refer to the ORF50P3 and ORF50P8 locations, respectively. (C) Overexpression of Egr-1 activates ORF50P via interacting with ORF50P3 and ORF50P8 domains. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with a combination of three vectors, one from the following groups: (i) pcDNA3.1(+) or egr-1/pcDNA3.1(+), (ii) the control vector, pRL-TK, and (iii) empty pGL3 vectors or pGL3 vectors encoding FL ORF50P or one of several deletions (Δ-2922 to -2044; Δ-2922 to -1322; Δ-2922 to -894; and Δ-2922 to -169). After 48 h post-transfection, the cells were lysed, and relative luciferase activity was monitored. Firefly luciferase was normalized to the corresponding Renilla luciferase activity. The luciferase activation of pGL3 by egr-1/pcDNA3.1(+) was represented as 1-fold. Each point denotes the average ± SD of three experiments. Columns with different alphabets are statistically significant (P<0.05) by least significant difference (LSD).