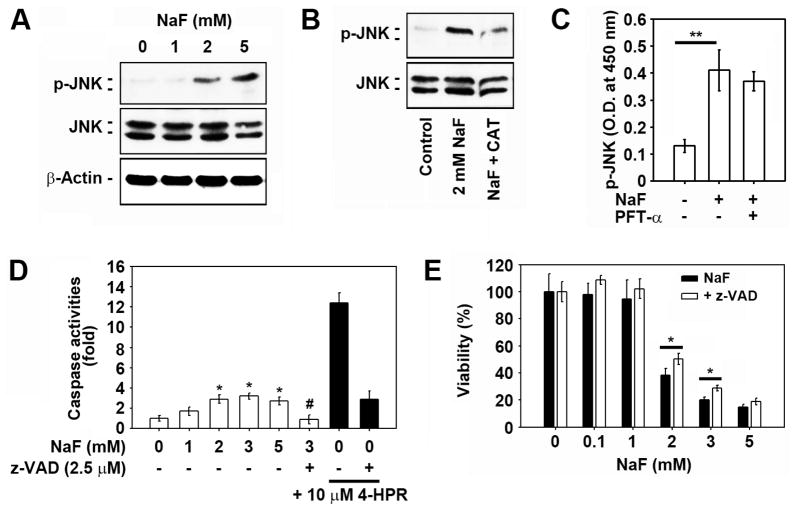
Fig. 5. JNK and caspase activation is at least in part associated with NaF-induced toxicity in mESCs.
(A) Cells were exposed to the increasing doses (0–5 mM) of NaF for 12 h and then processed for western analysis. Cells were also exposed to the indicated concentrations of NaF in the presence and absence of 2,500 U/ml CAT or 5 μM PFT-α for 12 h and then the (B) levels of p-JNK and total JNK protein, and (C) activity of JNK were detected using western blot analysis and enzyme immunometric assays. In addition, cells were exposed to the indicated concentrations of NaF in the presence and absence of 2.5 μM z-VAD-fmk or 10 μM 4-HPR for 24 h, and (D) caspase 3/7 activities in the lysates or (E) cell viability was analyzed. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. the experiments. In panel D, *p < 0.05 and #p < 0.05 indicate significant differences from the untreated control cells and the 2 mM NaF treatment alone, respectively.