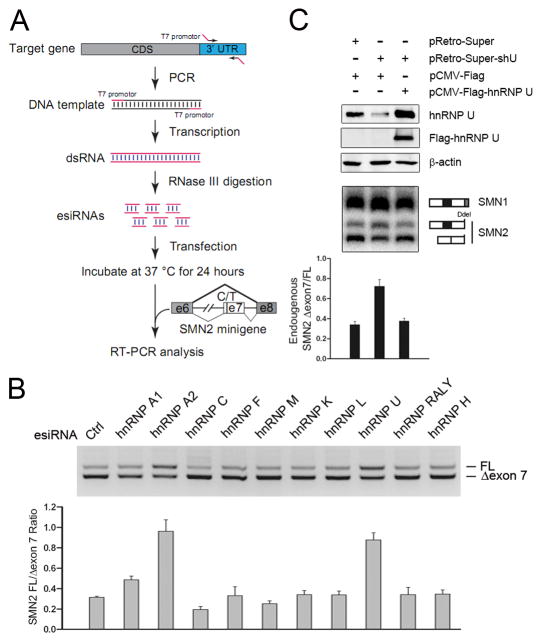
Figure 1. Identification of hnRNP U as a potent splicing regulator from an esiRNA screen.
(A) The scheme of the esiRNA screen strategy. Specific regions in the 3′UTR of individual RBPs (Table S1) were PCR-amplified and in vitro transcribed into dsRNAs. The long dsRNAs were digested with purified RNase III and small dsRNAs purified from native PAGE. Individual small dsRNAs were co-transfected with the SMN2 minigene reporter carrying the alternative exon 7 in HeLa cells and the products were analyzed by RT-PCR. (B) Results of a representative panel of hnRNP proteins from the esiRNA screen. The effects were quantified in the bottom panel. (C) Rescue of the splicing response to hnRNP U RNAi with a FLAG-tagged, RNAi-resistant version of hnRNP U. Cleavage by Dde I was used to distinguish the PCR products of the SMN2 pre-mRNA and spliced mRNA from that of spliced SMN1 mRNA. The results were quantified and shown at bottom. Data in B and C are shown as mean ± SD.