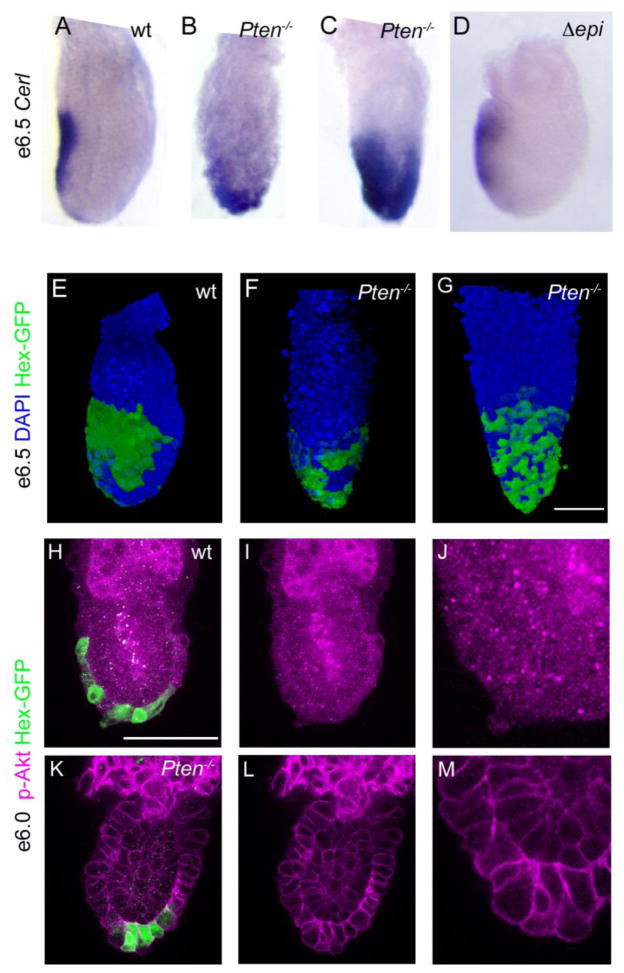
Figure 5. AVE cells remain distal or are evenly dispersed over the embryonic region in Pten null embryos.
(A–D) e6.5 embryos, anterior to the left. Cer1, a marker of the AVE, is expressed on the anterior of the wild-type embryo (A). In 37% of Pten−/−mutant embryos (11/30) (B), most Cer1-expressing cells remain near the distal tip of the embryo. In an additional 13% of Pten−/−mutant embryos (4/30) Cer1 expression appears to cover most of the embryonic region (C). Cer1 is expressed in the anterior of Pten-epiblast deleted embryos (D; 4/4 embryos). (E–G) Hex-GFP expression (stained with anti-GFP antibody (green); DAPI is blue) in e6.5 embryos, anterior to the left. In wild-type (E), Hex-expressing cells form a contiguous group on the anterior, proximal side of the embryo, while Hex-expressing cells remain distal in Pten−/− mutants (F) or are scattered over the embryonic region (G), similar to the Cer1 expression pattern. (H–M) Staining for phospho-Akt (S473) (magenta) in wild-type (H–J) and Pten−/− (K–M) e6.0 embryos. Phospho-Akt was detected at a high level at the membrane of visceral endoderm cells in Pten−/− embryos, but was not detected above background in the membrane of visceral endoderm cells in the embryonic region of wild-type embryos. The Hex-GFP+ cells are near the distal tip of the mutant embryo, but have migrated toward the anterior in wild type at this stage. (I–J, L–M) p-Akt signal only; high magnification views in J and M. Scale bars in A–G, H–I and K–L = 100μm.