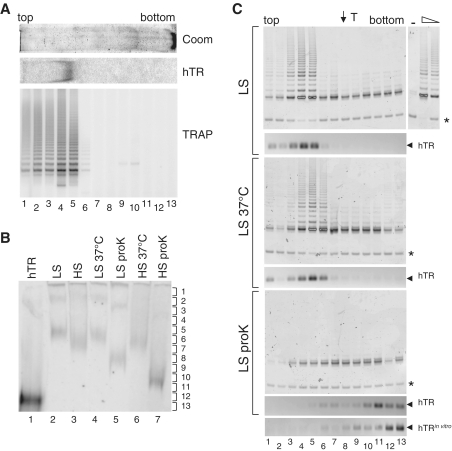
Figure 1.
Telomerase purification via affinity selection and native gel electrophoresis. (A) Co-migration of hTR and telomerase activity after native gel electrophoresis of affinity-purified Raji cell extract (at 0.1 M NaCl). After clear native gel electrophoresis, one lane was stained with Coomassie blue (top panel; gel slice oriented from top to bottom as indicated), and one lane probed with a radiolabelled probe corresponding to hTR after transfer to nylon (middle panel). A third lane was sliced into 13 fractions, eluted into buffer and subjected to the telomere repeat amplification protocol, TRAP (bottom panel). (B) Relative mobility of telomerase after native gel electrophoresis and detection with a radiolabelled probe corresponding to hTR. Lane 1, in vitro transcribed hTR alone; Raji cell extracts purified at 0.1 M NaCl (low stringency; LS) and 0.6 M NaCl (high stringency; HS) at 4°C (lanes 2 and 3, respectively), 37°C (lanes 4 and 6) and after incubation with proteinase K (lanes 5 and 7). Brackets at right indicate position of gel slices. (C) The indicated treatments as in (B) were resolved by native gel electrophoresis, sliced into 13 fractions and subjected to TRAP (upper panels) and RT–PCR analysis to detect the native mobility of hTR (lower panels). Thyroglobulin (T) was loaded onto an adjacent lane of the native gel; its position is indicated with an arrow, top. Asterisk indicates TRAP internal PCR standard; arrows at right, hTR. The bottom panel represents PCR detection of hTR after native gel electrophoresis of purified, in vitro transcribed hTR alone (no added extract). At right, 1.0 and 0.2 µl of rabbit reticulocyte lysate (RRL) containing reconstituted telomerase activity, or water alone (−) as positive and negative controls for TRAP, respectively.