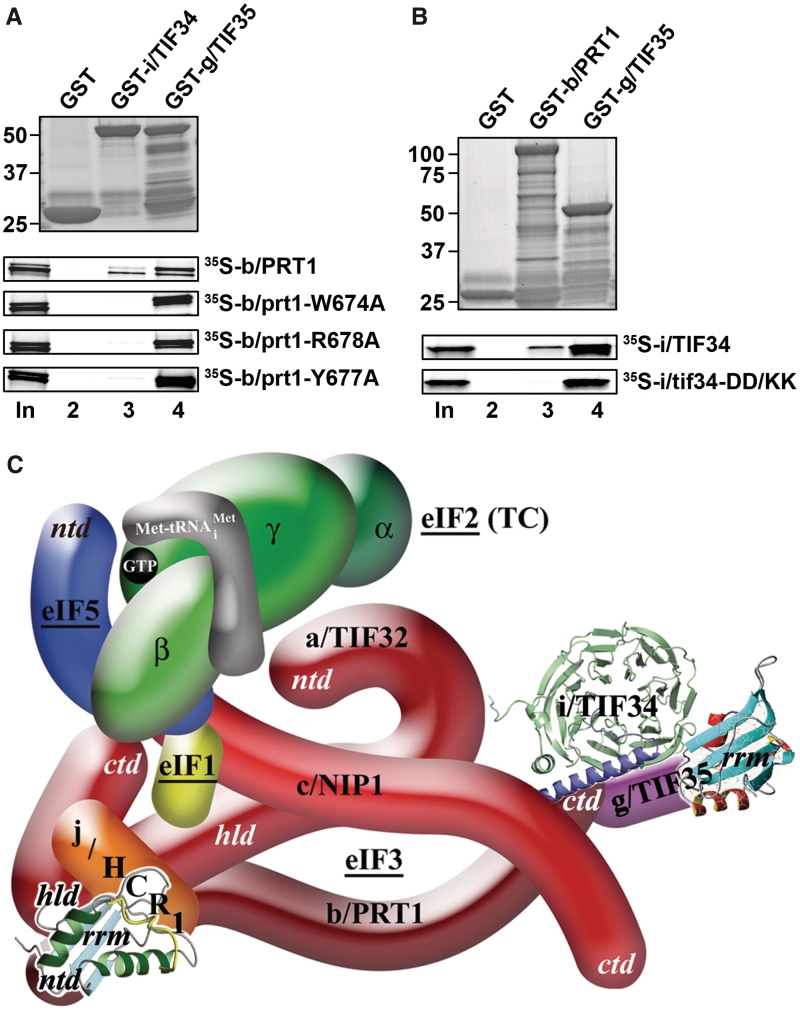
Figure 4.
The tif34-DD/KK mutation impairs the direct interaction between i/TIF34 and b/PRT1 in vitro and the revised 3D model of eIF3 in the MFC. (A) The prt1-W674A, -Y677A, and -R678A mutations impair the direct interaction between b/PRT1 and i/TIF34 in vitro. Full-length i/TIF34 (lane 3) and g/TIF35 (lane 4) fused to GST, and GST alone (lane 2), were tested for binding to 35S-labeled wt b/PRT1 and its mutant derivatives; 10% of input amounts added to each reaction is shown in lane 1 (In). (B) Full-length b/PRT1 (lane 3) and g/TIF35 (lane 4) fused to GST, and GST alone (lane 2), were tested for binding to 35S-labeled wt i/TIF34 and the DD/KK mutant derivative. (C) A revised 3D model of eIF3 and its associated eIFs in the MFC (based on the data from (9); ntd, N-terminal domain; ctd, C-terminal domain; hld, HCR1-like domain; rrm, RNA recognition motif; TC, ternary complex). The NMR structure of the interaction between the RRM of human eIF3b (green and light blue) and the N-terminal peptide of human eIF3j (yellow) (12), the NMR structure of the C-terminal RRM of human eIF3g (red and sky-blue) (5), and the X-ray structure of the yeast i/TIF34–b/PRT1 complex (this study), were used to replace the original schematic representations of the corresponding molecules.