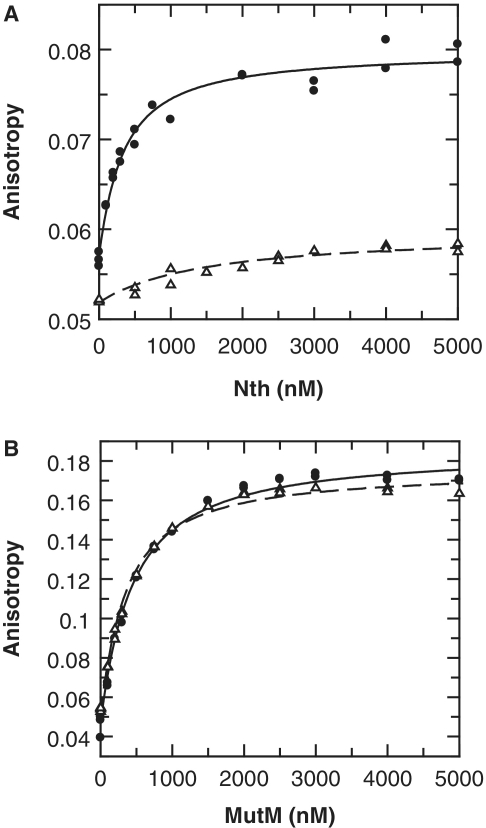
Figure 3.
Binding of Nth and MutM to AP sites. Neisserial Nth and MutM enzymes were tested for binding to double-stranded 5′ HEX labelled oligonucleotides containing either an abasic furanose analogue or a non-specific sequence (AP·G and C·G, respectively; Table 1). Binding was determined by titrating increased amounts of enzyme into oligonucleotide (100 nM) and monitoring both fluorescence anisotropy and intensity. Binding of Nth lead to a significant decrease in HEX intensity that gives a distortion in the observed anisotropy (35): to compensate for this both anisotropy and intensity data were simultaneously fitted (Supplementary Figure S1), only anisotropy is shown here for clarity. (A) Binding of Nth is shown with the best fit to a single-site binding equation for AP·G (solid circles, Kd = 286 nM), and for C·G (open triangles, Kd = 1440 nM). (B) Binding of MutM is shown with the best fit to a single-site binding equation for AP·G (solid circles, Kd = 386 nM), and for C·G (open triangles, Kd = 303 nM).