Figure 4.
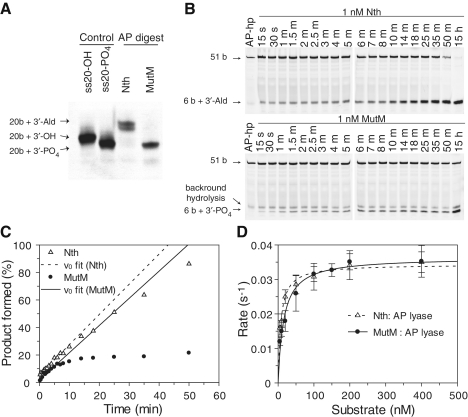
Cleavage of AP sites by Nth and MutM, and their products. (A) The products of Nth and MutM AP lyase activities were established by analysing reactions with the 50-AP substrate (see ‘Materials and Methods’ section) on a 20% denaturing polyacrylamide gel, and comparison with ss20-OH and ss20-PO4 oligonucleotides. Observed migrations fit with those previously observed for 3′-Ald and 3′-PO4 lesions (33), the dual band observed with the 3′-Ald is typical and likely due to different tautomers of the unsaturated aldehyde. (B) Typical steady-state reaction profiles are shown with AP-hp substrate (see ‘Materials and Methods’ section) for reactions with 1 nM Nth or MutM and 100 nM AP-hp substrate, showing accumulation of product over time. (C) Steady-state reactions were quantified by fluorescence scanning of gels, and the reaction profiles were fitted to a linear equation for the initial phase of the reaction; reactions with Nth (open triangles; dashed line) go to completion, while those for MutM (solid circles; solid line) are inhibited by product formation. (D) Steady-state analyses with AP-hp are shown with the best fit to the Michaelis–Menten equation for Nth (open triangles with a dashed line, kcat = 0.034 ± 0.001/s and Km = 7.5 ± 1 nM), and for MutM (solid circles with solid line, kcat = 0.036 ± 0.002/s and Km = 15.7 ± 0.3 nM). Error bars show the SD for experiments performed on a minimum of three occasions.