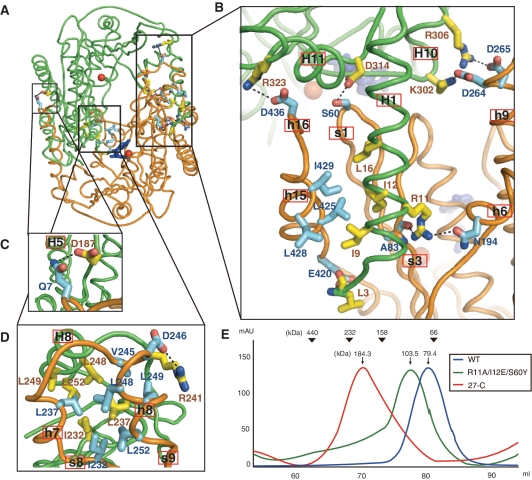
Figure 3.
Structural analyses of the dimeric interface. (A) Overall view of the Pf NurA dimeric interface. Two different Pf NurA subunits are colored in green and orange.(B) A close-up view of the first interface of Pf NurA dimer. In the first interface, one subunit (green) and another Pf NurA (orange) interact primarily through the N- and PIWI domains as described in the text. (C) In addition to these interactions, an ion pair Gln7–Asp187 is present. (D) In the second interface, helices H7 and H8 of one Pf NurA interact with helices h7 and h8 of another Pf NurA. Strands s8 and s9 are also involved in dimer formation. Oxygen and nitrogen atoms are shown in red and blue, respectively. (E) Comparison of the oligomeric states of the wild-type and dimeric interface Pf NurA mutants using gel filtration chromatography. Standard molecular weights are shown at the top. Gel filtration analysis (Superdex 200) was performed using a buffer containing 25 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.4), 200 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol and 5 mM DTT.