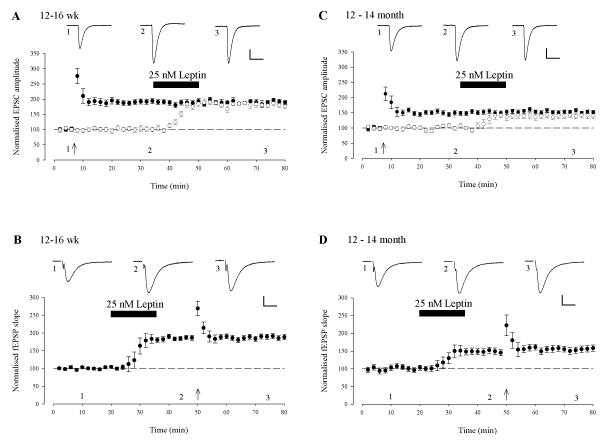
Figure 6. Leptin induced LTP and classical Hebbian LTP share similar expression mechanisms.
A, C. Activity-dependent LTP occludes leptin induced LTP. Plot of the pooled data of the normalized EPSC amplitude against time in 12-16 week (A) and 12-14 month (C) old slices. A pairing protocol (100Hz for 1sec paired with postsynaptic depolarisation) was given to the test pathway (filled circle) at the time indicated by the arrow and this resulted in LTP. Subsequent addition of leptin (25 nM; 15 min) failed to induce any further increase in synaptic transmission in this path. In the control pathway (open circle), addition of leptin resulted in LTP and the magnitude of this effect was not significantly different to the potentiated pathway. B,D. Leptin-induced LTP occludes activity-dependent LTP. Plot of the pooled data of the normalized fEPSP slope against time in 12-16 week (B) and 12-14 month (D) old slices. Application of leptin resulted in a persistent increase in synaptic transmission that was unaffected by the subsequent LTP-inducing protocol.