Abstract
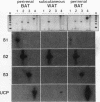
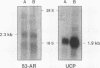
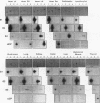
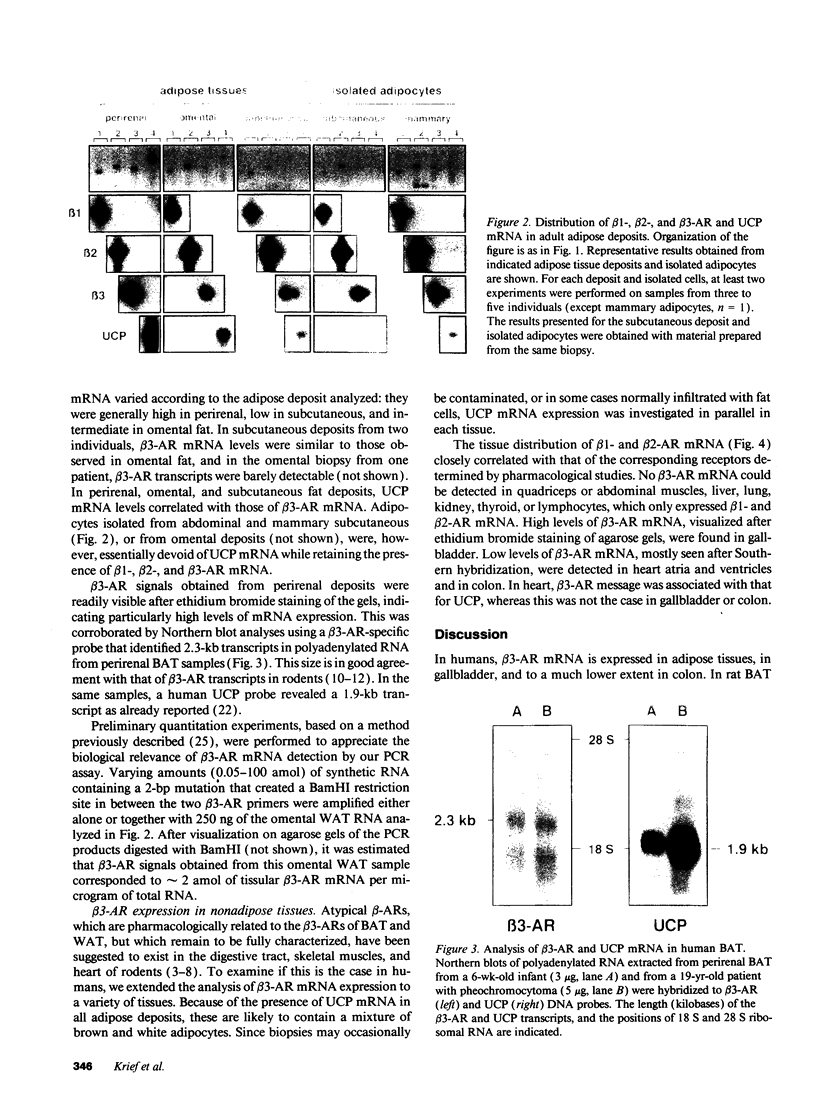
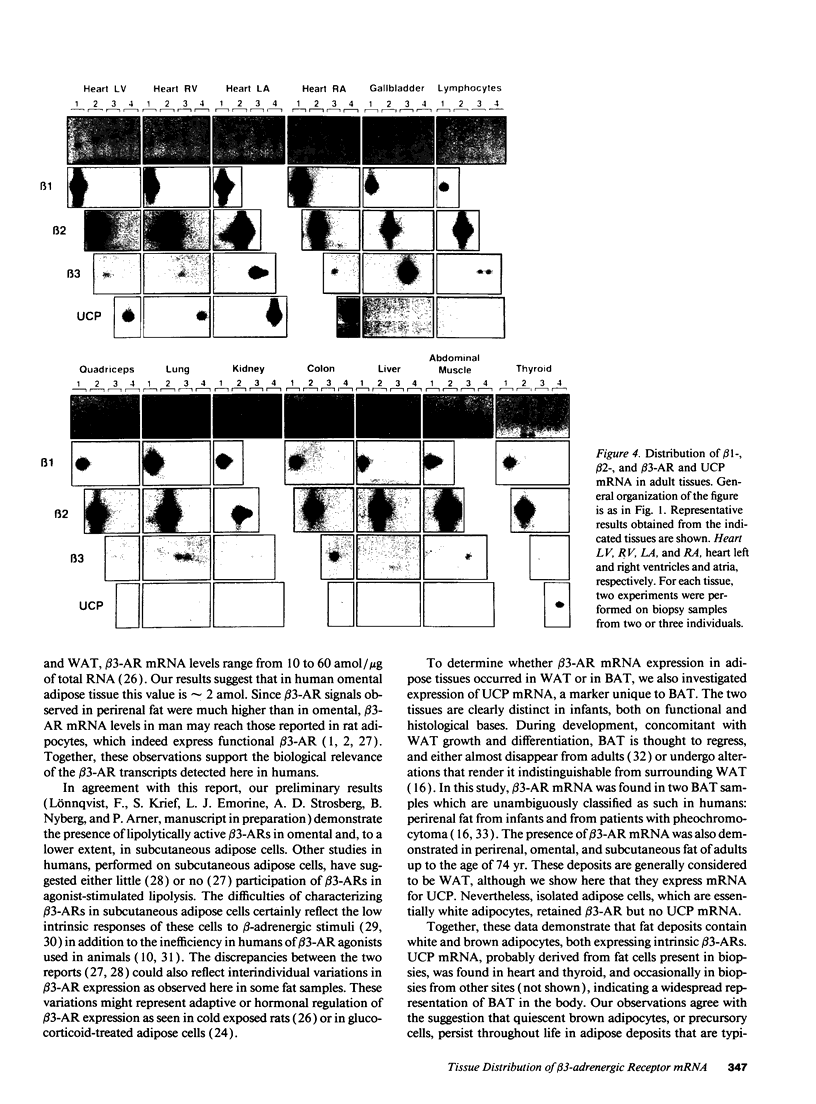
Expression of mRNA for beta 1-, beta 2-, and beta 3-adrenergic receptors (beta 1-, beta 2-, and beta 3-AR) was investigated in human tissues. beta 1- and beta 2-AR mRNA distribution correlated with that of the cognate receptors established by pharmacological studies. beta 3-AR transcripts were abundant in infant perirenal brown adipose tissue, characterized by the presence of uncoupling protein (UCP) mRNA. In adult whole adipose tissues, beta 3-AR mRNA levels were high in deep deposits such as perirenal and omental, and lower in subcutaneous. In these deposits, UCP mRNA levels paralleled those of beta 3-AR. However, isolated omental and subcutaneous adipose cells, enriched in white adipocytes, expressed beta 3-AR but no UCP transcripts. beta 3-AR mRNA was highly expressed in gallbladder, and to a much lower extent in colon, independently of UCP mRNA. Quadriceps or abdominal muscles, heart, liver, lung, kidney, thyroid, and lymphocytes did not express intrinsic beta 3-AR mRNA. This study demonstrates that substantial amounts of brown adipocytes exist throughout life in adipose deposits, which are generally classified as white. These deposits are the main sites of beta 3-AR expression, which also occurs in gallbladder and colon. beta 3-AR may thus be involved in the control of lipid metabolism, possibly from fat assimilation in the digestive tract, to triglyceride storage and mobilization in adipose tissues.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akli S., Chelly J., Lacorte J. M., Poenaru L., Kahn A. Seven novel Tay-Sachs mutations detected by chemical mismatch cleavage of PCR-amplified cDNA fragments. Genomics. 1991 Sep;11(1):124–134. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90109-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arch J. R. The brown adipocyte beta-adrenoceptor. Proc Nutr Soc. 1989 Jul;48(2):215–223. doi: 10.1079/pns19890032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker-André M., Hahlbrock K. Absolute mRNA quantification using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). A novel approach by a PCR aided transcript titration assay (PATTY). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9437–9446. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchetti A., Manara L. In vitro inhibition of intestinal motility by phenylethanolaminotetralines: evidence of atypical beta-adrenoceptors in rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):831–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Clarke D. E. Agonist and antagonist characterization of a putative adrenoceptor with distinct pharmacological properties from the alpha- and beta-subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):723–734. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassard A. M., Bouillaud F., Mattei M. G., Hentz E., Raimbault S., Thomas M., Ricquier D. Human uncoupling protein gene: structure, comparison with rat gene, and assignment to the long arm of chromosome 4. J Cell Biochem. 1990 Jul;43(3):255–264. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240430306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Leighton B., Wilson S., Thurlby P. L., Arch J. R. An investigation of the beta-adrenoceptor that mediates metabolic responses to the novel agonist BRL28410 in rat soleus muscle. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 1;37(5):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champigny O., Ricquier D., Blondel O., Mayers R. M., Briscoe M. G., Holloway B. R. Beta 3-adrenergic receptor stimulation restores message and expression of brown-fat mitochondrial uncoupling protein in adult dogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10774–10777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman B. J., Farquahar D. L., Galloway S. M., Simpson G. K., Munro J. F. The effects of a new beta-adrenoceptor agonist BRL 26830A in refractory obesity. Int J Obes. 1988;12(2):119–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connacher A. A., Jung R. T., Mitchell P. E. Weight loss in obese subjects on a restricted diet given BRL 26830A, a new atypical beta adrenoceptor agonist. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1988 Apr 30;296(6631):1217–1220. doi: 10.1136/bmj.296.6631.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Marullo S., Briend-Sutren M. M., Patey G., Tate K., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg A. D. Molecular characterization of the human beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1118–1121. doi: 10.1126/science.2570461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engfeldt P., Hellmér J., Wahrenberg H., Arner P. Effects of insulin on adrenoceptor binding and the rate of catecholamine-induced lipolysis in isolated human fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15553–15560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Lahners K. N., Chaudhry A. Molecular cloning and expression of the rat beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):895–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Lahners K. N. Differential adrenergic regulation of beta 1- and beta 3-adrenoreceptor messenger ribonucleic acids in adipose tissues. Endocrinology. 1992 Jan;130(1):109–114. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.1.1309320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henny C., Schutz Y., Buckert A., Meylan M., Jequier E., Felber J. P. Thermogenic effect of the new beta-adrenoreceptor agonist Ro 16-8714 in healthy male volunteers. Int J Obes. 1987;11(5):473–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumann A. J. Is there a third heart beta-adrenoceptor? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Aug;10(8):316–320. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus S., Casteilla L., Bouillaud F., Ricquier D. The uncoupling protein UCP: a membraneous mitochondrial ion carrier exclusively expressed in brown adipose tissue. Int J Biochem. 1991;23(9):791–801. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(91)90062-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langin D., Portillo M. P., Saulnier-Blache J. S., Lafontan M. Coexistence of three beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in white fat cells of various mammalian species. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 9;199(3):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90492-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauriège P., De Pergola G., Berlan M., Lafontan M. Human fat cell beta-adrenergic receptors: beta-agonist-dependent lipolytic responses and characterization of beta-adrenergic binding sites on human fat cell membranes with highly selective beta 1-antagonists. J Lipid Res. 1988 May;29(5):587–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin D. P., MacDonald A. Evidence for the existence of 'atypical' beta-adrenoceptors (beta 3-adrenoceptors) mediating relaxation in the rat distal colon in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):569–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14122.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mory G., Bouillaud F., Combes-George M., Ricquier D. Noradrenaline controls the concentration of the uncoupling protein in brown adipose tissue. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 30;166(2):393–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzzin P., Revelli J. P., Kuhne F., Gocayne J. D., McCombie W. R., Venter J. C., Giacobino J. P., Fraser C. M. An adipose tissue-specific beta-adrenergic receptor. Molecular cloning and down-regulation in obesity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24053–24058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahmias C., Blin N., Elalouf J. M., Mattei M. G., Strosberg A. D., Emorine L. J. Molecular characterization of the mouse beta 3-adrenergic receptor: relationship with the atypical receptor of adipocytes. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3721–3727. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04940.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G., Locke R. M. Thermogenic mechanisms in brown fat. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jan;64(1):1–64. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostman J., Arner P., Engfeldt P., Kager L. Regional differences in the control of lipolysis in human adipose tissue. Metabolism. 1979 Dec;28(12):1198–1205. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricquier D., Nechad M., Mory G. Ultrastructural and biochemical characterization of human brown adipose tissue in pheochromocytoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Apr;54(4):803–807. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-4-803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricquier D., Raimbault S., Champigny O., Miroux B., Bouillaud F. Comment to Shinohara et al. (1991) FEBS Letters 293, 173-174. The uncoupling protein is not expressed in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 25;303(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taneja D. T., Clarke D. E. Evidence for a noradrenergic innervation to "atypical" beta adrenoceptors (or putative beta-3 adrenoceptors) in the ileum of guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jan;260(1):192–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate K. M., Briend-Sutren M. M., Emorine L. J., Delavier-Klutchko C., Marullo S., Strosberg A. D. Expression of three human beta-adrenergic-receptor subtypes in transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Mar 14;196(2):357–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaagsma J., Nahorski S. R. Is the adipocyte beta-adrenoceptor a prototype for the recently cloned atypical 'beta 3-adrenoceptor'? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Jan;11(1):3–7. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]