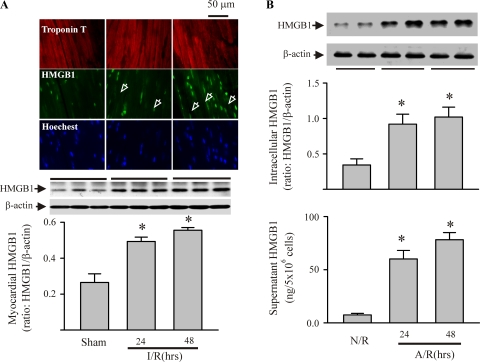
Fig. 1.
Ischemia-reperfusion (I/R)-induced myocardial expression of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) in vivo and anoxia-reoxygenation (A/R)-induced myocyte production and release of HMGB1 in vitro. A: mice were challenged with I/R or sham procedures. Mouse hearts were harvested 24 and 48 h after the reperfusion for detection of HMGB1 protein by immunohistochemistry and Western blot. Top: immunohistochemistry using fluorescence microscopy. Troponin T-antibody targeted myocytes, Hoechst targeted nuclei, and HMGB1-antibody targeted HMGB1. Images are representatives of three separate experiments (original magnification ×63). Arrowheads indicate cytoplasmic HMGB1. Middle and bottom: Western blot assessment for myocardial HMGB1: exact blots (middle), and densitometric analyses (bottom). Values are means ± SE; n = 3 mice/group. *P < 0.05 compared with sham. B: isolated cardiac myocytes were challenged with A/R or normoxia-reoxygenation (N/R). Myocytes and their supernatants were harvested 24 and 48 h after reoxygenation for evaluation of HMGB1 expression with Western blot (top) and release of HMGB1 extracellularly by ELISA (bottom). For the Western blot assay, representative blots are shown at top, and densitometry analyses are shown at bottom. Values are means ± SE; n = 4. *P < 0.05 compared with N/R.