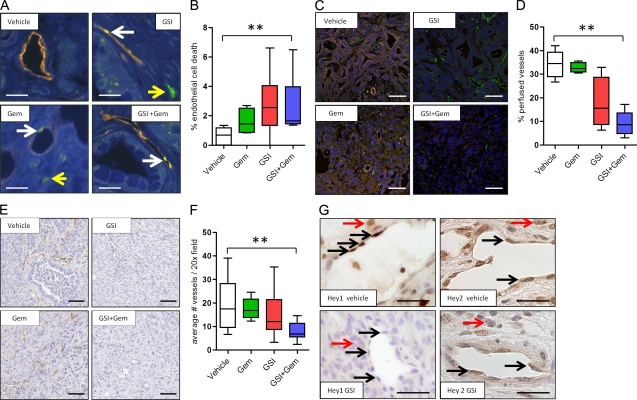
Figure 4.
The combination of MRK003 and gemcitabine synergistically kills intratumoral endothelial cells to decrease vascular function and density in PDA. (A) Representative immunofluorescence images of DAPI (blue), Meca32 (orange), and Cleaved caspase 3 (CC3; green) content in each of the 3 d–treated cohorts (n = 3 or more samples evaluated for each cohort). White arrows: CC3-positive endothelial cells; yellow arrow: CC3-positive nonendothelial cell. Bars, 10 µm. (B) Percentage of CC3-positive Meca32-expressing endothelial cells in tumor samples treated for 3 d (**, P = 0.008). Vehicle, n = 5; gemcitabine, n = 4; GSI, n = 6; GSI and gemcitabine, n = 6. (C) Representative immunofluorescence images of DAPI (blue), Meca32 (green), and Lectin (red) content in each of the 3 d–treated cohorts (bars, 50 µm; n = 3 or more samples evaluated for each cohort). (D) Quantification of vascular patency (percentage of lectin and meca32 positive endothelial cells) in the GSI/gemcitabine combination treatment (n = 5) compared with vehicle (n = 5; **, P = 0.008) or gemcitabine (n = 3; P = 0.004) GSI (n = 4; P = 0.06) compared with vehicle. (E) Histological representative Meca32 IHC-stained images for each of the cohorts of animals treated for 10 d. Bars, 50 µm. (F) Quantification of MVD in 3 d cohorts reveals a significant decrease in MVD in the GSI/gemcitabine combination treatment (n = 4) cohort compared with the gemcitabine (n = 4; P = 0.03), GSI (n = 4; P = 0.03), and vehicle (n = 8; **, P = 0.02) cohorts. All animals were sacrificed 1 h after the last dose of gemcitabine and 6 h after the last dose of the GSI. (G) Expression of Hey1 and Hey2 protein in the tumor endothelial cells of mice treated with vehicle or GSI. Black arrows: positive endothelial nuclei; red arrows: positive nonendothelial KPC tumor nuclei. Bars, 10 µm. n = 3 for each cohort. Error bars represent SEM.