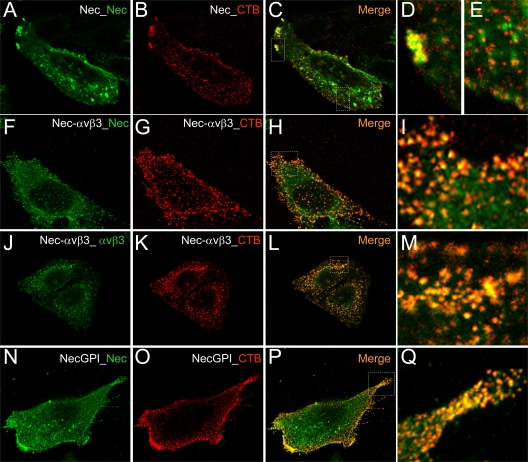
Fig 3.
Localization of nectin1 and αVβ3-integrin at lipid rafts, as detected by colocalization with CT-B (cholera toxin B) by confocal microscopy. CHO cells transiently overexpressing nectin1 alone (Nec) (A to E), nectin1 plus αVβ3-integrin (Nec-αVβ3) (F to M), or nectin-GPI (NecGPI) (N to Q) were labeled using a Vybrant lipid raft-labeling kit (Invitrogen). Live cells were incubated for 10 min at 4°C with recombinant CT-B, rinsed several times with chilled phosphate-buffered saline, and incubated with anti-CT-B rabbit antibody for 15 min at 4°C. After several rinses, cells were paraformaldehyde fixed, permeabilized with Triton X-100, and then stained for the presence of nectin1 (green) (A, F, and N) by means of MAbs R1.302 and CK35 for nectin1 or MAb L230 for αVβ3-integrin (J), followed by anti-mouse fluorescein isothiocyanate-coupled antibody. CT-B was stained with anti-rabbit DyLight 549 (red) (B, G, K, and O). Cells were mounted with Fluoromount and observed with a Leica TCS-SL confocal microscope. Images were collected with a 63× oil immersion objective (numerical aperture, 1.62); confocal slices were 0.7 to 1.5 μm thick; confocal microscopy was performed as previously detailed (1). Panels C, H, L, and P show merged images. Panels D, E, I, M, and Q show enlargements of the white dotted rectangles in panels C, H, L, and P, respectively.