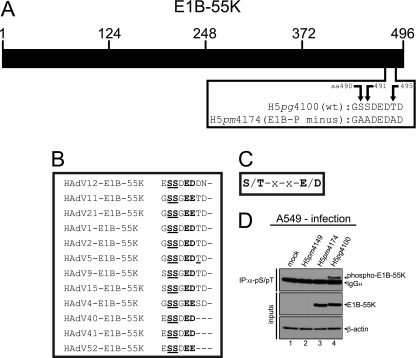
Fig 1.
CK2 phosphorylation consensus motif of E1B-55K and E1B-55K phosphorylation. (A) Schematic representation of E1B-55K showing the amino acid sequence of the C terminus of E1B-55K in H5pg4100 (wt) and the H5pm4174 (E1B-P minus) mutant. (B) Alignment of E1B-55K C-terminal amino acid sequences from different adenovirus types. Amino acids highly conserved throughout different E1B-55K proteins and known to be phosphorylated in HAdV5 are underlined. Amino acids matching the general CK2 consensus motif are in bold. (C) Simplified CK2 consensus motif according to Meggio et al. (36) and Pinna et al. (46). A serine or threonine in boldface denotes CK2-targeted amino acids in this motif. (D) A549 cells were mock infected or infected with H5pm4149 (E1B minus), the E1B-P minus mutant H5pm4174 and H5pg4100 wt virus at an MOI of 20 FFU per cell. Total cell lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-phosphoserine/phosphothreonine (pS/pT) antibody. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected by immunoblotting with anti-E1B antibody 2A6. Steady-state concentrations (inputs) of E1B-55K and β-actin were determined by immunoblotting of protein extracts with anti-E1B-55K (2A6) and anti-β-actin (AC-15). The Western blot represents one experiment which had been independently repeated at least four times.