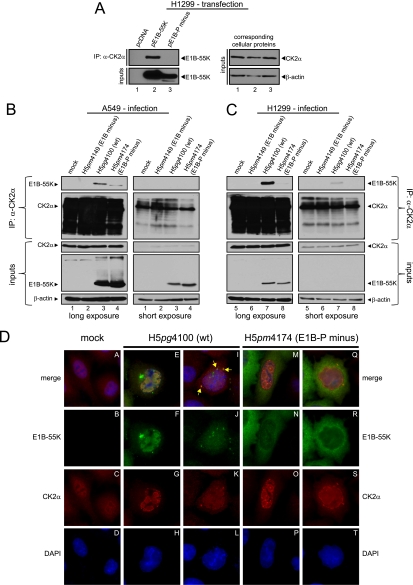
Fig 3.
Coimmunoprecipitation and indirect immunofluorescence to analyze E1B-55K and its interaction with CK2α in infected cells. (A) CK2α interaction with E1B-55K after transfection. H1299 cells transfected with empty plasmid vector (pcDNA) and vectors encoding E1B-55K (pE1B-55K) or mutant E1B-55K (pE1B-P minus) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with an anti-CK2α antibody (ab13410). Proteins separated by SDS-PAGE were detected by Western blots with anti-E1B antibody (2A6). Western blot analyses of protein input levels are shown below for E1B-55K (2A6) and to the right for CK2α (ab13410) and β-actin (AC-15). (B and C) CK2α interaction with E1B-55K during infection. A549 and H1299 cells either mock infected or infected (MOI = 20 FFU/cell) with H5pm4149 (E1B minus), H5pg4100 (wt), and H5pm4174 (E1B-P minus) virus were analyzed by immunoprecipitation assays using protein A-Sepharose-coupled anti-CK2α antibody (ab13410). Proteins separated by SDS-PAGE were detected by immunoblotting with anti-E1B (2A6) and anti-CK2α (ab13410) antibodies. Immunoblot analyses of protein input levels are shown below for CK2α, E1B-55K (2A6), and β-actin (AC-15). (D) CK2α is relocalized during adenoviral infection. A549 cells either mock infected or infected with the indicated viruses (MOI = 20 FFU/cell) were analyzed by in situ immunofluorescence staining for E1B-55K (2A6), CK2α (ab13410), and DNA content (DAPI). Examples of the two major CK2α relocalization patterns observed in this cell line are shown (n = 168).