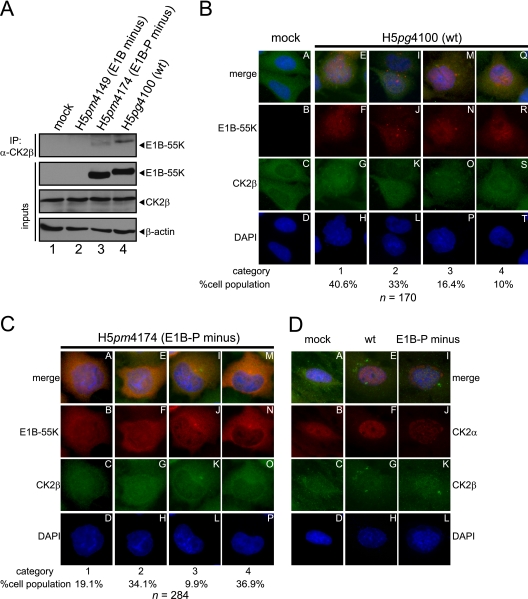
Fig 4.
Coimmunoprecipitation and indirect immunofluorescence to analyze E1B-55K and its interaction with CK2β in infected cells. (A) CK2β interaction with E1B-55K during infection. A549 cells either mock infected or infected (MOI = 20 FFU/cell) with H5pm4149 (E1B minus), H5pg4100 (wt), or H5pm4174 (E1B-P minus) virus were analyzed by immunoprecipitation assays using protein A-Sepharose-coupled anti-CK2β antibody (Santa Cruz, “51”). Proteins separated by SDS-PAGE were detected by immunoblotting with anti-E1B (2A6) antibody. Immunoblot analyses of protein input levels are shown below for CK2β (6D5), E1B-55K (2A6), and β-actin (AC-15). (B and C) CK2β is relocalized during adenoviral infection. A549 cells either mock infected or infected with the indicated viruses (MOI = 20 FFU/cell) were analyzed by in situ immunofluorescence staining for E1B-55K (7C11), CK2β (6D5), and DNA content (DAPI). Examples of the four major CK2β relocalization patterns observed in this cell line are shown (B, n = 170; C, n = 284). (D) Comparison of CK2α and CK2β localization during adenoviral infection. A549 cells either mock infected or infected with the indicated viruses (MOI = 20 FFU/cell) were analyzed by in situ immunofluorescence staining for CK2α (ab13410), CK2β (6D5), and DNA content (DAPI). Presented are blots and immunofluorescence data which show results that have been reproduced in at least three independent experiments.