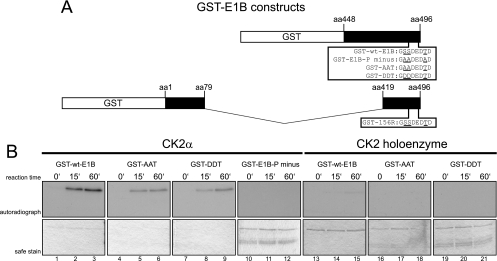
Fig 7.
CK2α, but not the CK2 holoenzyme, phosphorylates E1B-55K's C terminus in vitro. (A) C-terminal amino acid sequences of different GST-E1B fusion proteins used in the phosphorylation assays. Underlined are amino acids known to be phosphorylated and/or changed to the indicated amino acids. Numbers above the schematic drawing represent amino acid (aa) positions of E1B-55K from which the GST fragments are derived. (B) The indicated GST-E1B fusion proteins were incubated either with recombinant CK2α or with CK2 holoenzyme together with radioactive [γ-32P]ATP for the indicated reaction times at 30°C. Kinase assays performed with the holoenzyme contained double the amount of substrate (GST-wt-E1B, GST-E1B-P minus, GST-AAT, and GST-DDT) and holoenzyme units compared to CK2α assays. After extensive washing, kinase assay samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie stained (“safe stain,” lower panels), and the gels were vacuum dried for autoradiographic detection with X-ray films (upper panels). Autoradiographs represent one of at least four independent experiments.