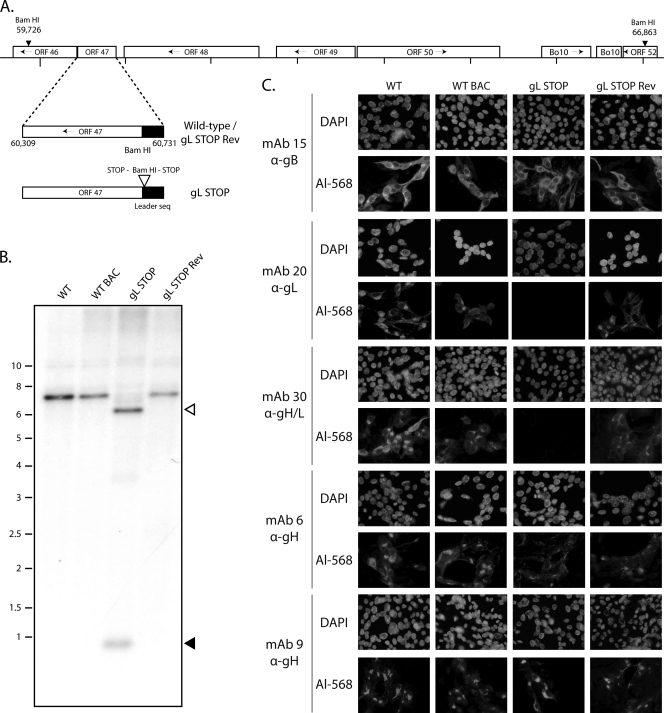
Fig 2.
Generation of a gL-deficient BoHV-4 mutant. (A) Schematic representation of the strategy followed to produce the recombinant BoHV-4 strain. The gL-deficient BoHV-4 mutant was derived from a cloned BoHV-4 BAC by the galK counterselection method. The gL coding sequence (ORF47) was disrupted by inserting stop codons near the end of the coding sequence for its predicted signal peptide (gL STOP). The mutation incorporated a new BamHI restriction site. (B) Verification of the molecular structure. Viral DNA was digested with BamHI, resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis, and hybridized with a 32P-labeled probe, corresponding to nucleotides 60087 to 61334. Open arrows show the restriction fragment that contains gL STOP. The 7,137-bp wild-type (WT) band becomes 6,553 bp for the gL STOP mutant. Black arrows show the remaining 620-bp fragment. Marker sizes (in kbp) are indicated on the left. (C) Glycoprotein expression by the gL-deficient BoHV-4 strain. MDBK cells were infected with the WT, the WT BAC, gL STOP, and gL STOP Rev BoHV-4 (MOI of 0.5 PFU per cell). Thirty-six hours postinfection, the cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained with MAb 15 (gB), MAb 20 (gL), MAb 30 (gH-gL), MAb 6 (gH), or MAb 9 (gH). An Alexa 568-conjugated goat anti-mouse secondary antibody was then used. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI.